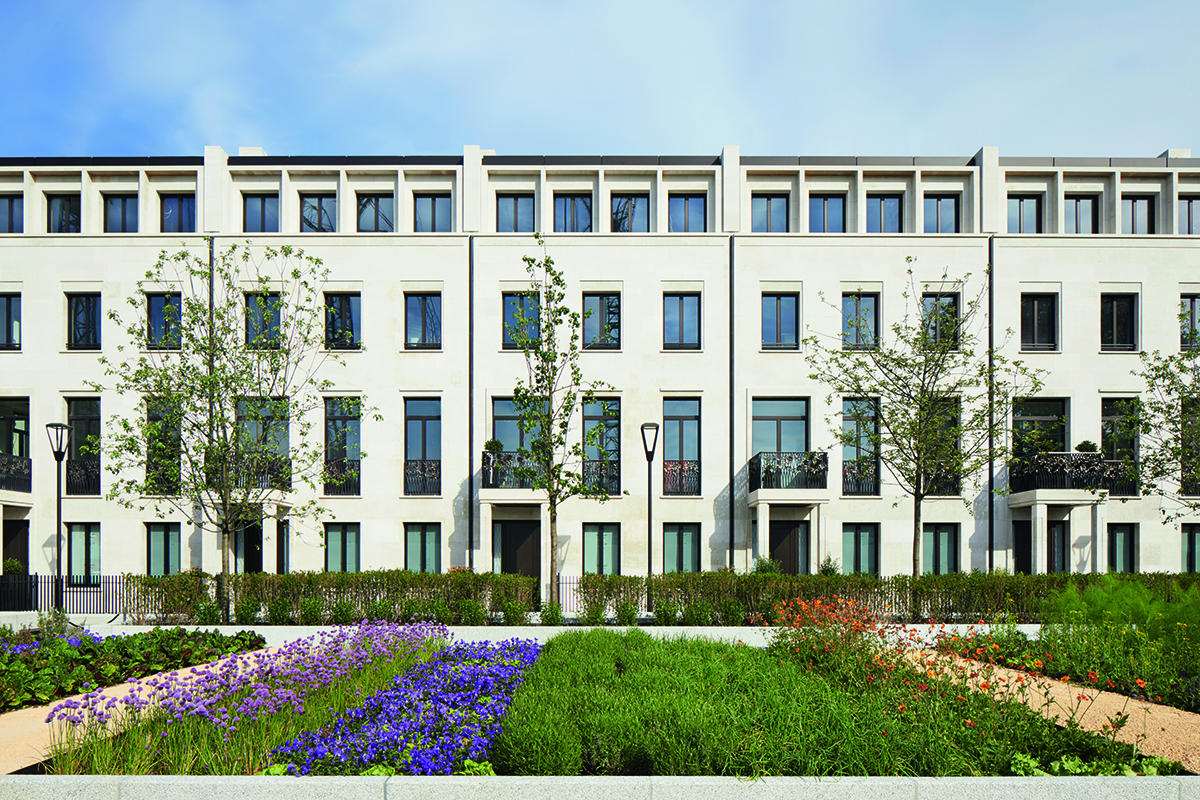

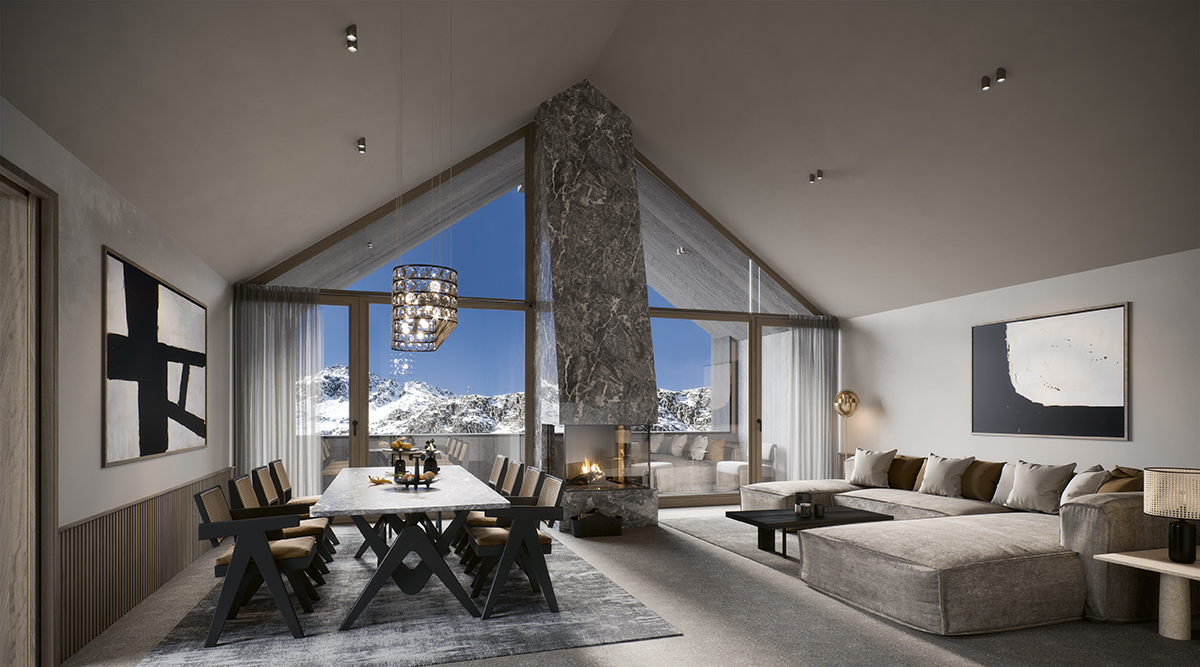
Mulberry Square townhouses at Chelsea Barracks
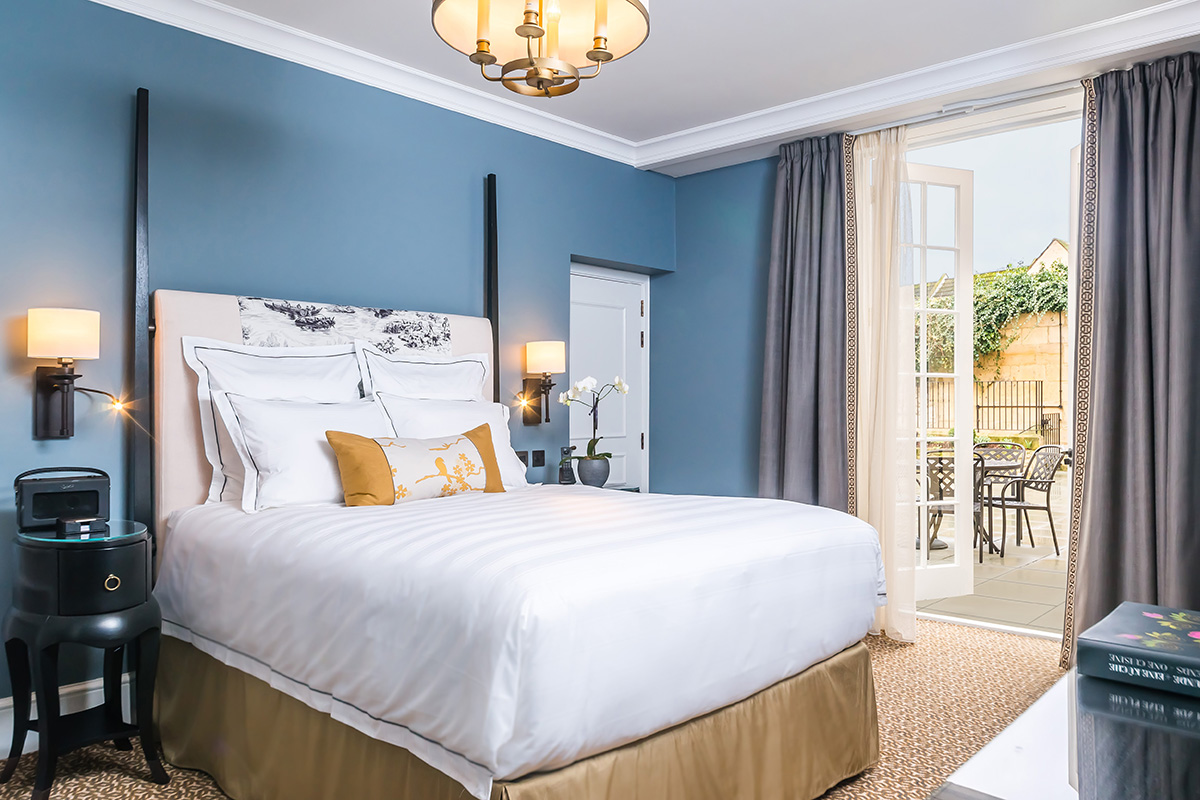
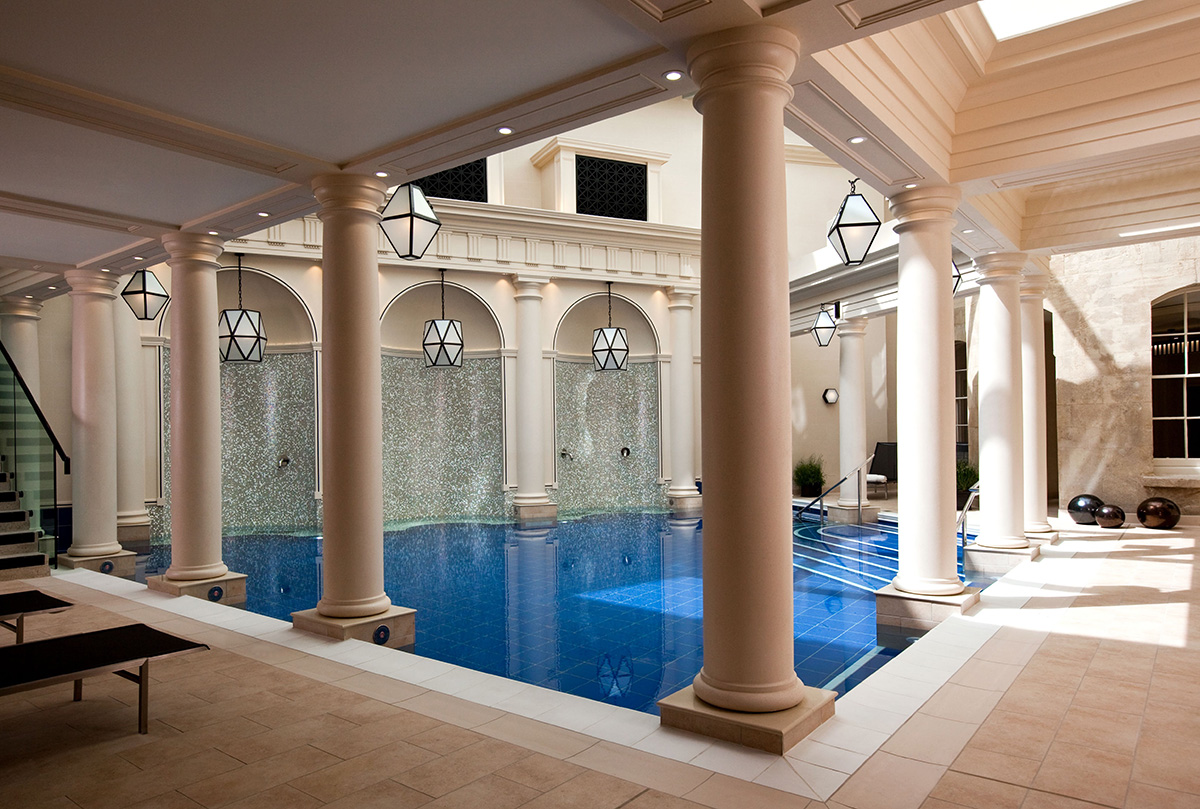
The exclusive Chelsea Barracks residential development in London aims to be the epitome of contemporary luxury living. It also draws on a wealth of traditional artisanal craft heritage, from specially designed and made oak furniture to bespoke light fittings, to forge a new historically significant landmark, as Mark C. O’Flaherty discovers
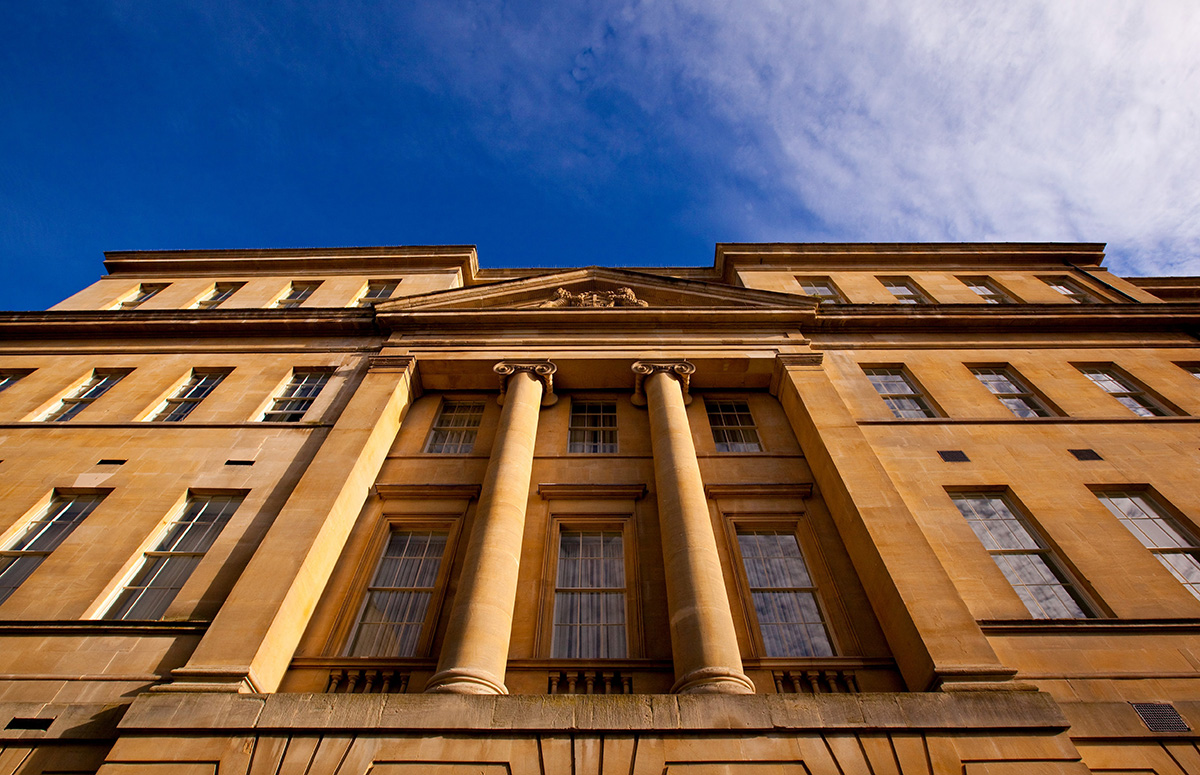
Some of the heftiest books lining the shelves of the world’s libraries are devoted to the history of London. The tale of Chelsea Barracks warrants a whole chapter of its own. It is an epic story, with handsome accents. Built as a home to Victorian infantry battalions, the original architecture stood for nearly 100 years. Since the 1960s, various plans for the site have been discussed but not materialised, but today Chelsea Barracks is a landmark again – a residential development that combines contemporary British craft with heritage inspiration. From the public artwork in the grounds to the finishings, light fittings and balustrades of the townhouses, Qatari Diar have brought together a nation of artisans.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The ongoing story of British craft is told from numerous perspectives, and has culminated in more than just a landmark – there is also The Chelsea Barracks Collection. Under the direction of Albion Nord, the studio responsible for the overall look of the townhouse show-home interiors, an 11-piece capsule of designs has been commissioned from many of the artisans involved. Each object is handmade and represents the highest level of British craftsmanship, creating a dialogue with the Georgian squares of Belgravia. Wine glasses and tumblers echo the glassware produced in the 18th century, while the Belgravia Lamp references the Doric, Ionic and Corinthian columns of local buildings. “It is inspired by the orders of classical architecture,” explains Ottalie Stride, creative director at Albion Nord. “It has strong London connotations.”
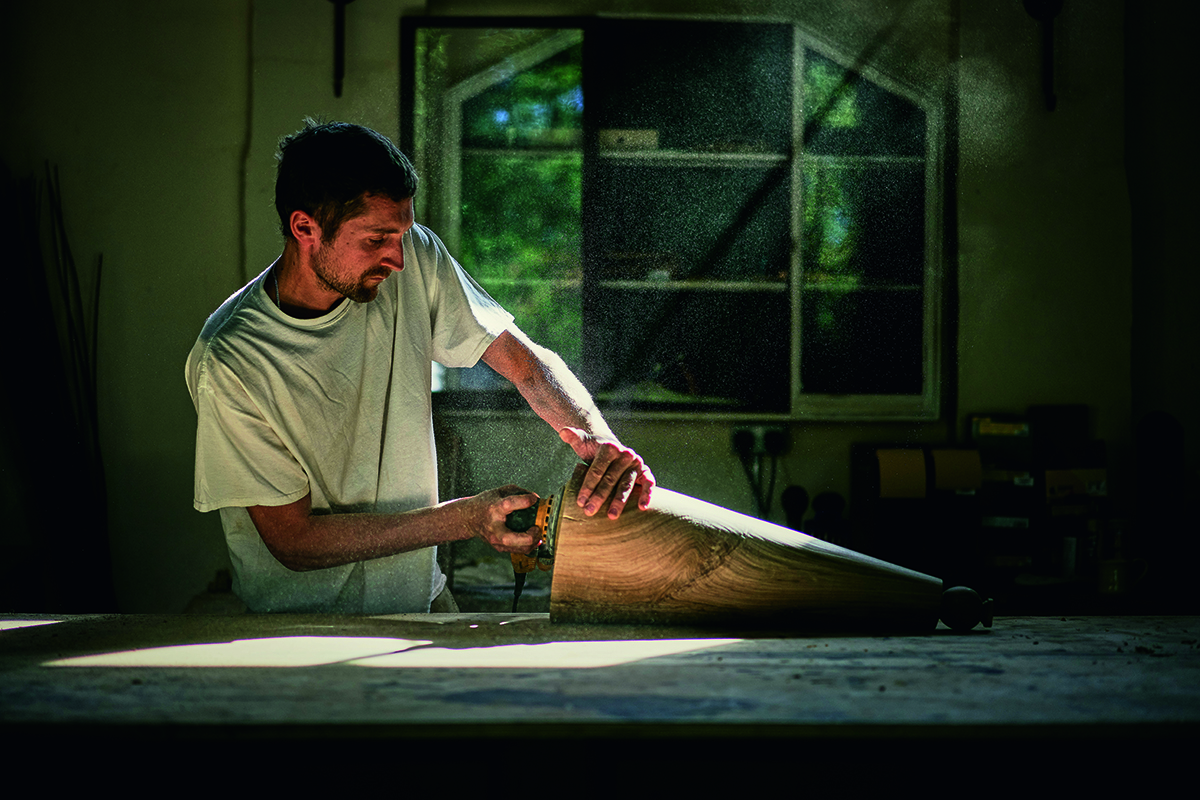
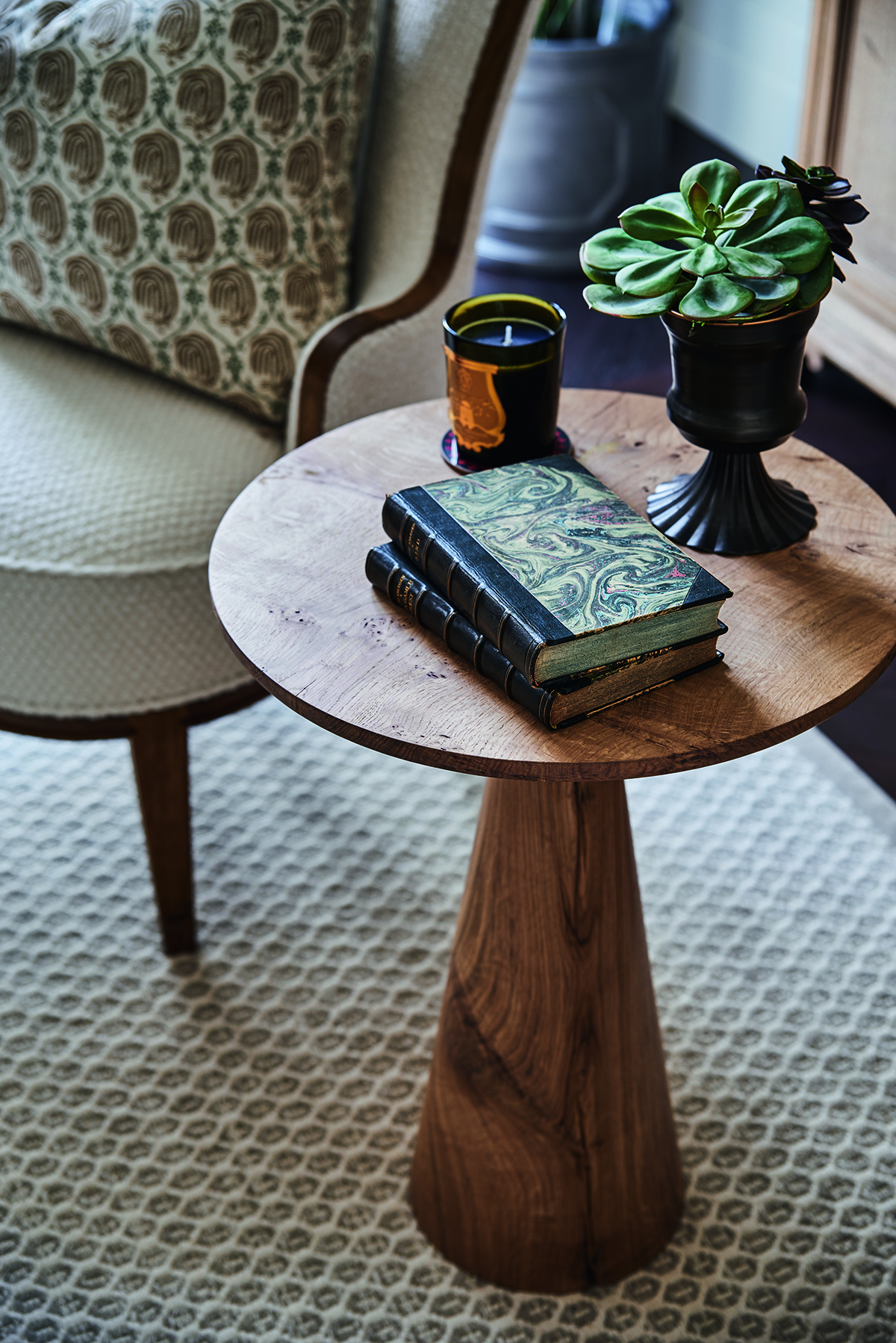


The Chelsea Barracks Collection, designed by Albion Nord, includes the Elizabeth Side Table made by Rory Stride (above) of Stride & Co
You can see the broader strokes of the style in London-based designer Tord Boontje’s floral elements on the townhouse balconies – the wild roses, peonies and apple blossom of the British countryside, so often showcased at the nearby Chelsea Flower Show – all forged in metal by West Country Blacksmiths, based in a 17th-century workshop in Somerset. From the physicality of their creation, to the greenery of Belgravia, they connect numerous threads within the narrative of Chelsea Barracks. These aren’t things you can take home – they are home.
Boontje’s work to date has been almost exclusively for interiors, so to have his petals adorning a façade is significant. They also form a link with the landscaping outside. From one of Boontje’s balconies you have a radiant view over the perfect floral grids planted by award-winning landscape gardener Jo Thompson and landscape architect Neil Porter. This is one of the most arresting and modern green spaces in the city today.
Read more: How Andermatt Swiss Alps is drawing a new generation of visitors
The best kind of design is often site-specific, taking visual cues from and creating a dialogue with its setting. All of the artisans involved in the development studied the site, its environment and and history. Using designs by Albion Nord, the artisans at Marina Mill created for The Chelsea Barracks Collection silkscreened upholstery in a diamond pattern that references tiling inside the restored Garrison Chapel on the grounds. Other designs by Albion Nord took inspiration from the floor plan of the Royal Hospital Chelsea. As much as upholstery, Marina Mill have been weaving history, too.
Chelsea Barracks is a style and brand as well as a prestigious residential address. The Chelsea Barracks Collection incorporates many elements that link the development to history. A metal and leather pendant lantern is inspired by the flashlights used by soldiers in the first world war, while the Barracks Bench has been created in homage to the Egypt-mania that captured London society in the 18th and 19th centuries. A collection of ceramics, titled Radnor, play on the history of porcelain in the area. Silversmith Nicholas Sprimont was the founder of the Chelsea Porcelain Factory, which from the mid 1740s became the tableware maker for the royal family. “They were the first important porcelain pottery manufacturer in England, so it’s great to bring this material to life,” says Stride.
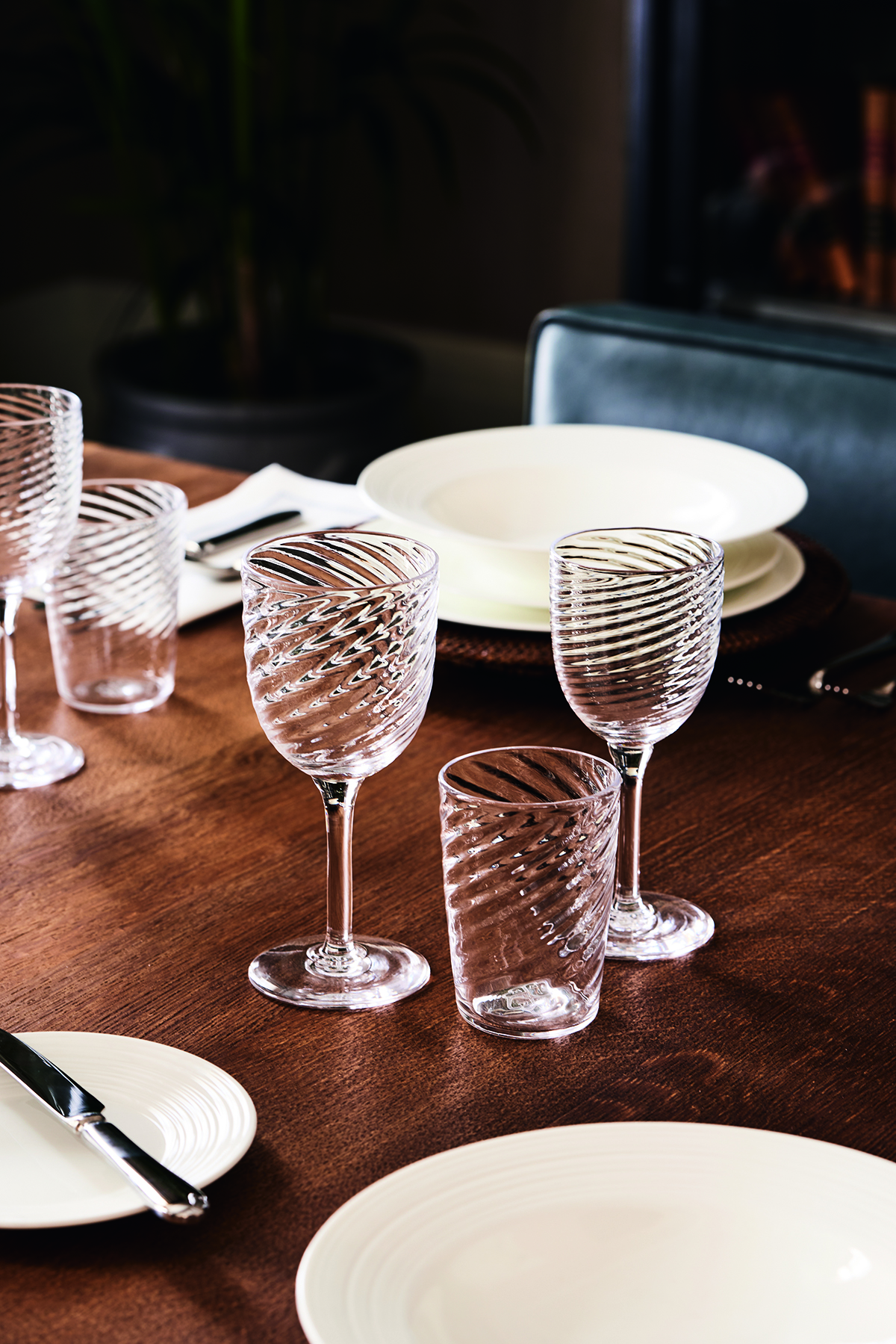
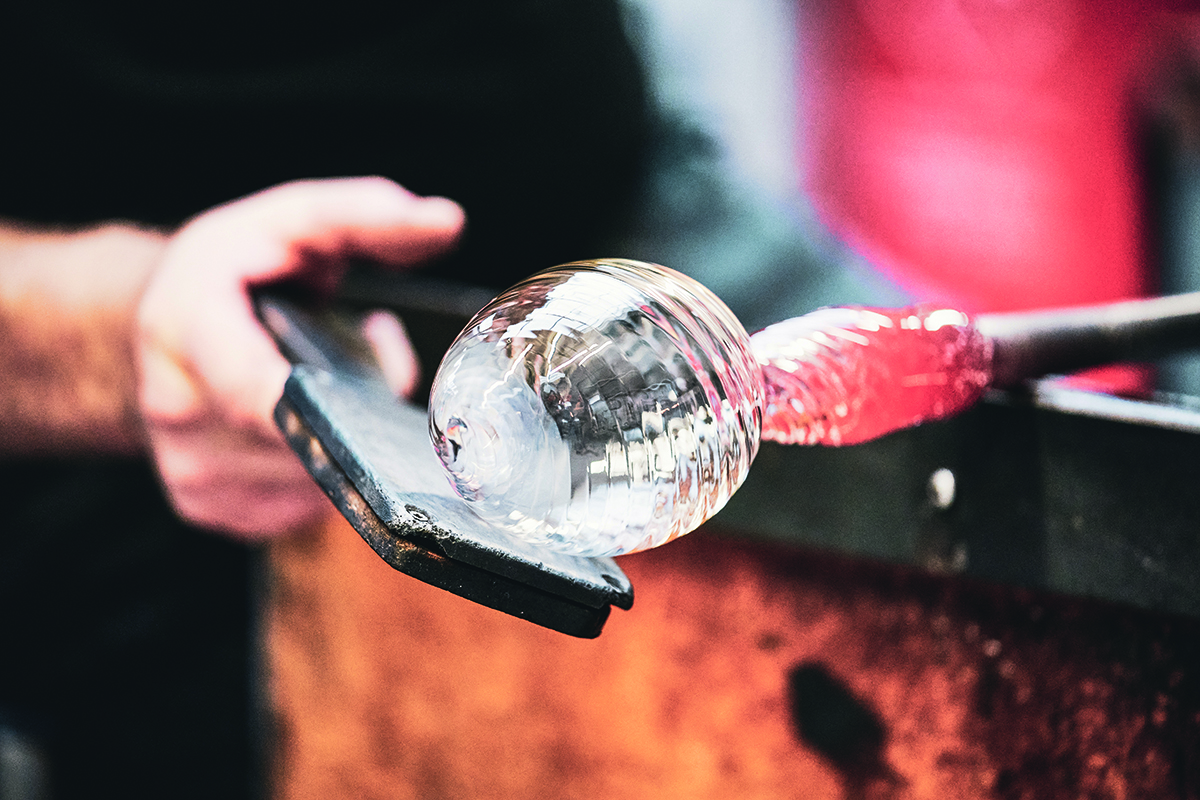


The Collection also includes Westminster glassware made by Stewart Hearn
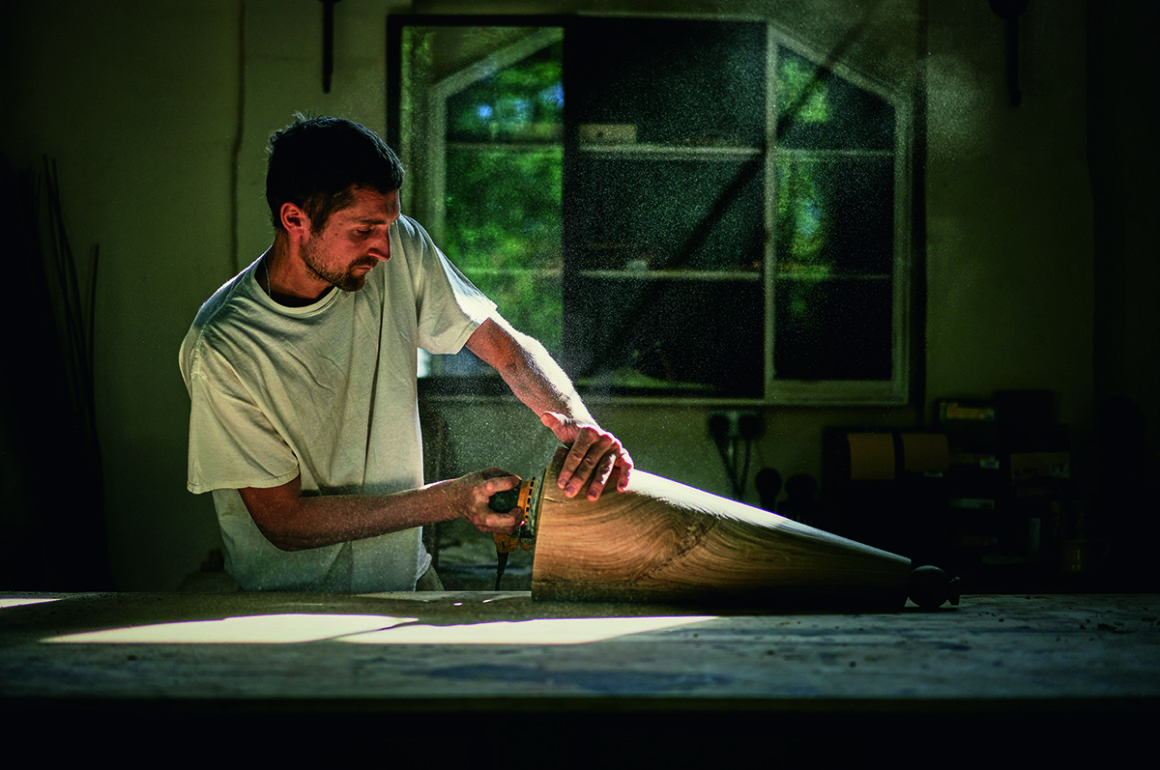
Some of the furniture created with the homes, and The Chelsea Barracks Collection, in mind – including a bench, bedside table, side table and writing desk – come from the Stride & Co workshops in West 38are beautifully crafted objects from carpenters accustomed to making only 15 to 20 pieces in a year. Each desk is made from a single piece of oak for consistency of grain. Detail is everything, and so is the story behind each piece – the side table is inspired by the British fondness for tea-drinking, which took hold in the mid 18th century. Other pieces are battalion inspired. “The Wellington Desk made by Stride & Co is inspired by a traditional campaign desk,” explains Stride. “It would have been used by officers and their staff during a military campaign. Our design here aims to retain the portability and simplicity of the original, whilst including special details such as the lion-claw feet and the Chelsea Barracks rose mark, featured on the key to both the desk and the bedside tables.”
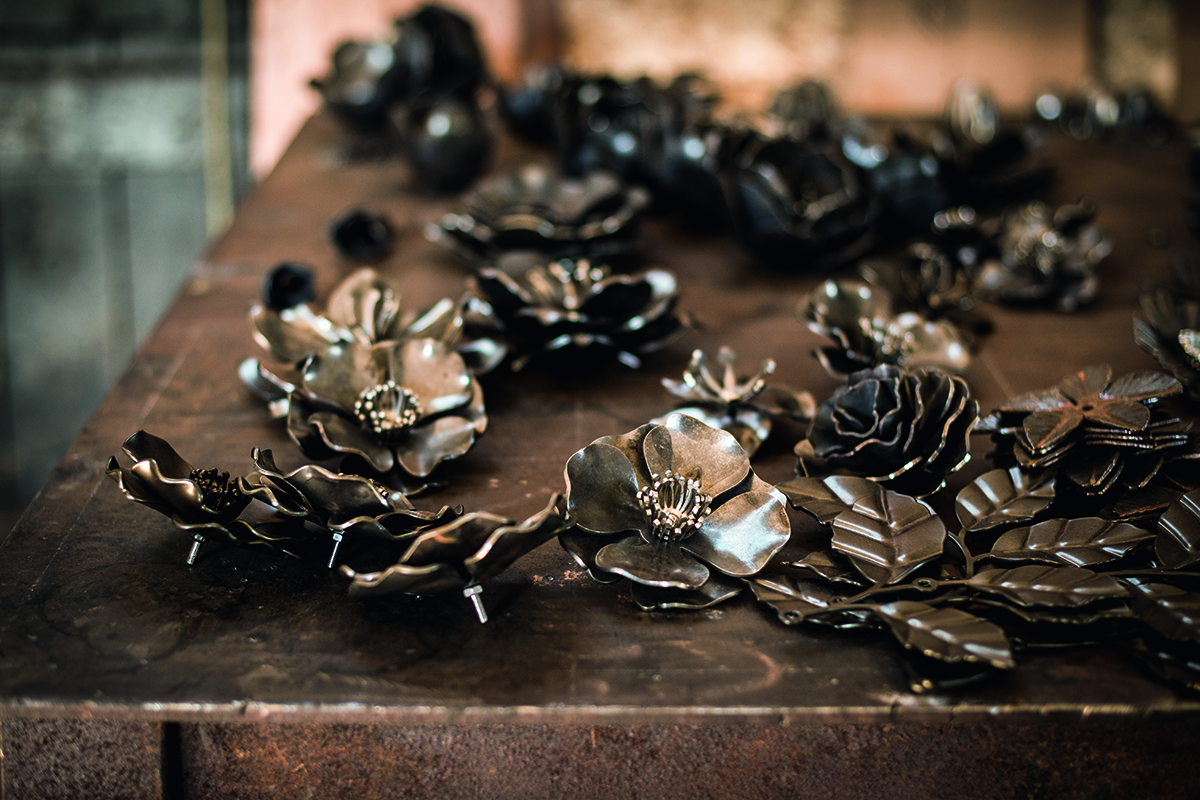
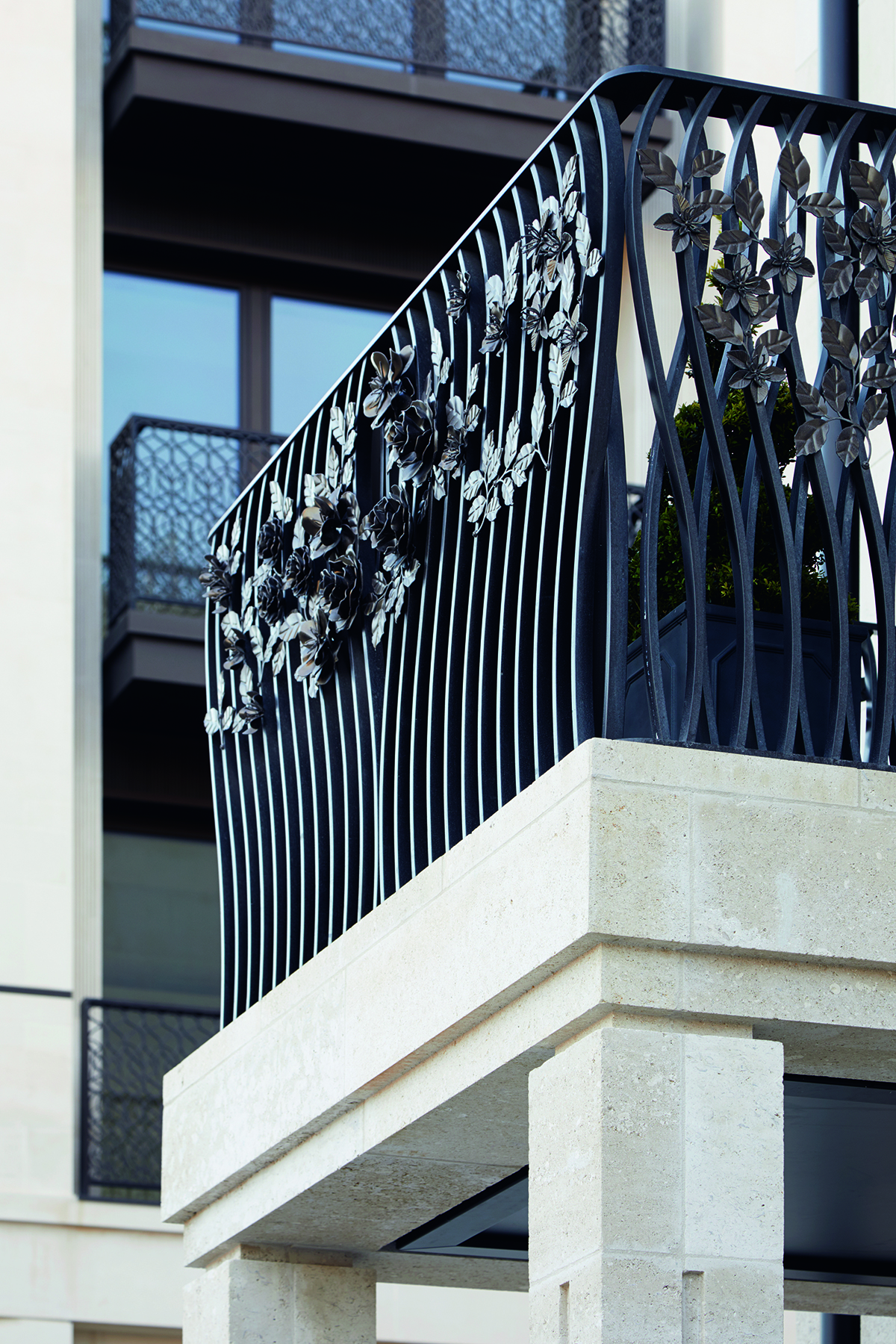


Tord Boontje’s specially commissioned metal floral decorations on the townhouse balconies
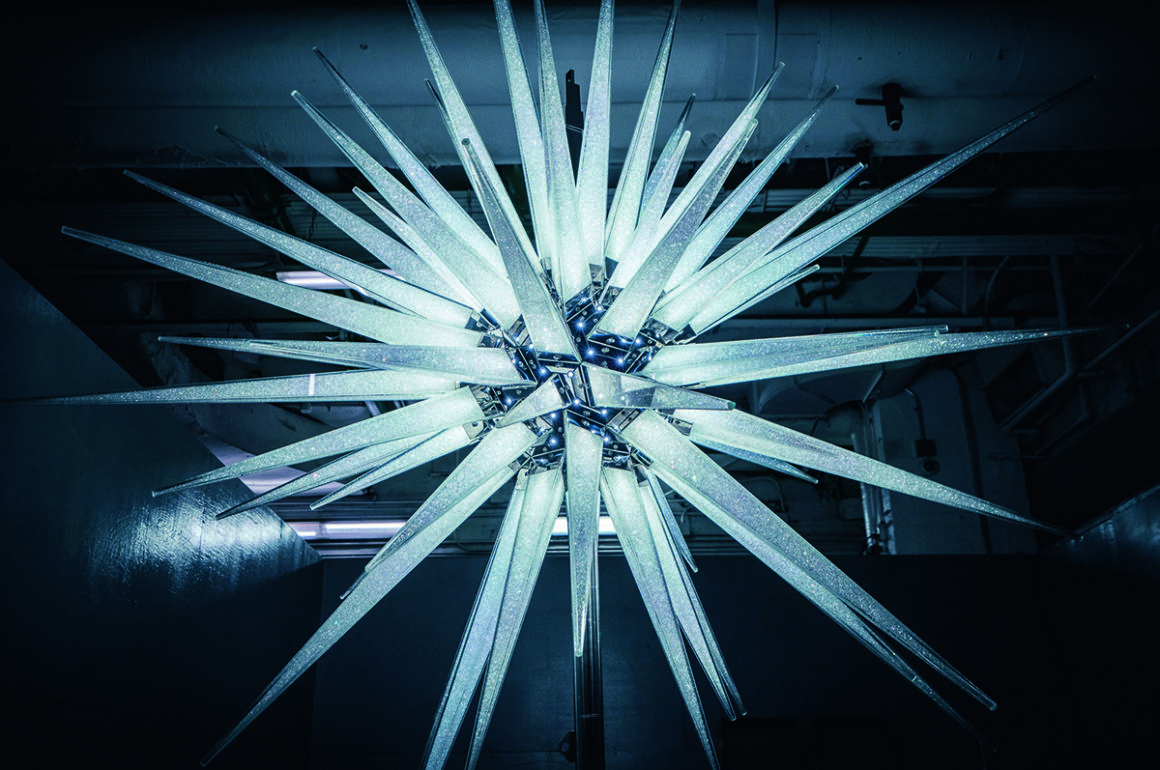
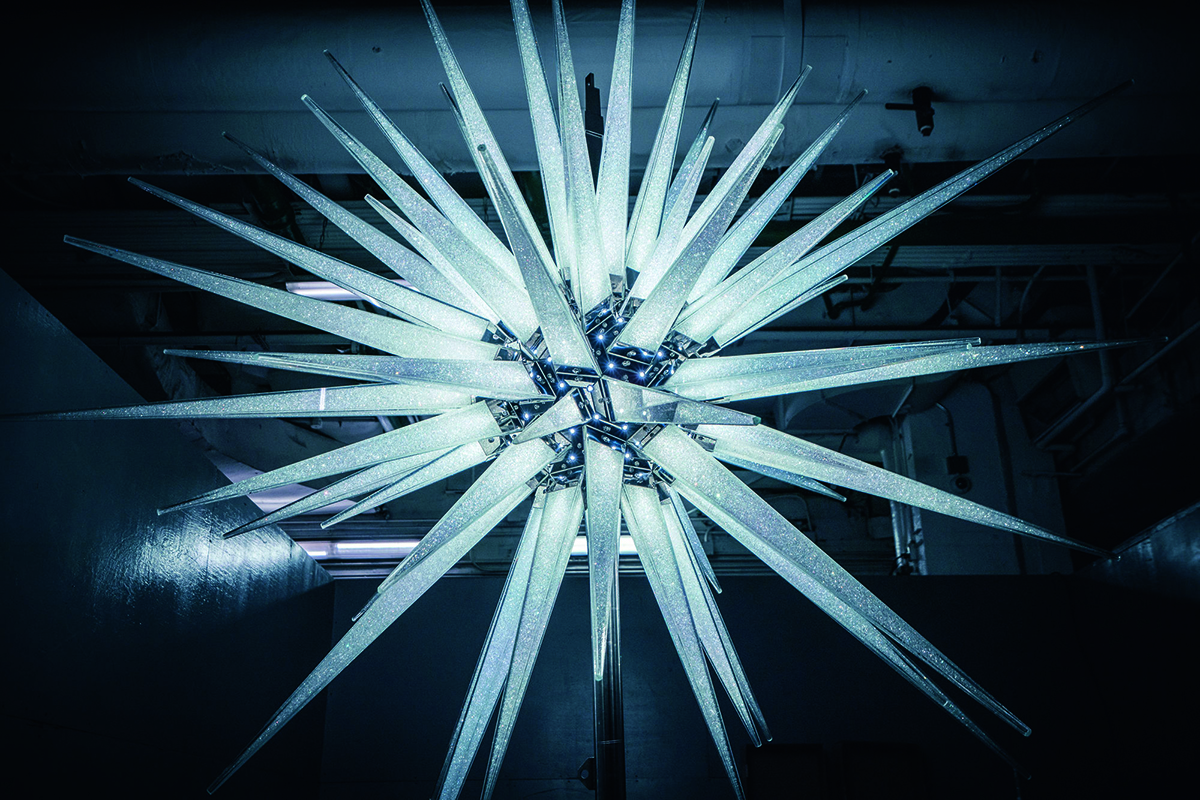
Like Boontje, bespoke light designer Sharon Marston looked to the history of the Chelsea Flower Show before starting work. Marston’s background flags up her instinctive approach to light and materials. Her career began in jewellery and costume design, working with Bella Freud, Paul Smith and the English National Opera. She creates objects that are luminescent, ethereal and elegant. The British flora is a constant inspiration. The two Willow chandeliers she created for Chelsea Barracks evoke the weeping willow tree found in the English countryside as well as landscapes by Turner and Constable. She was also keen to emphasise the inherent Britishness of the formal properties of her pieces. “Craftmanship is at the heart of my approach,” she explains. “The artisans I work with are small cottage industries dotted around the UK, ranging from glassblowers and ceramicists to metalwork engineers. My close relationship with each is what brings the intricate detail of my work to life. There are approximately 2,000 pieces of hand-crafted decorative components made from woven bronze mesh spread across both chandeliers, taking many weeks to create.”

Mulberry Square gardens, planted with fruits, herbs and flowers
Many of the works carried out for Chelsea Barracks pushed the boundaries for their creators. Reedway is an engineering company involved in the nuclear, space and marine industries. The ornate balustrades they created for the residences were inspired by the work of Arts and Crafts visionary William Morris and made using high-pressure water cutting on metal, usually employed in aviation, so making something very much 21st century. Reedway also worked on artist Conrad Shawcross’s tree-like sculpture at the development, Bicameral, constructed from anodised aluminium and installed permanently in the grounds.
What the designers and artisans behind the new Chelsea Barracks have done is take the romance of a classical Georgian home and refract it through the lens of today’s style but grounded it with Victorian muscle. The method in which that style has been crafted tells a story that has depth and longevity, one that will develop for generations to come.
Restoring the past

The Grade II listed Victorian iron railings during their restoration
The Victorian railings at Chelsea Barracks were given a pass when the government was requisitioning cast iron for the war effort in the 1940s. Grade II listed for more than ten years, the railings have now been restored to their original grandeur as part of the new development. The development team at Qatari Diar worked with the foundry Paterson Engineering in Scotland on what became a complex task. The original railings were moulded 150 years ago, and despite their apparent uniformity, there was no standard fitting. Each component had to be logged before removal for restoration. Back in their original place, they look magnificent. History has been refreshed and a link has been forged between the new architecture and the Victorian era that made these five hectares world famous. “They mark the border of Chelsea Barracks and pay homage to the history of the site,” explains Richard Oakes, Chief Sales and Marketing Officer Europe and Americas at Qatari Diar. “Together with the Garrison Chapel, the railings are now all that remain of the original 19th-century barracks, and their preservation and restoration has been a journey all of its own and one that we’re extremely proud of.”
Find out more: chelseabarracks.com
This article features in the Autumn 2020 Issue, hitting newsstands in October.








































































Recent Comments