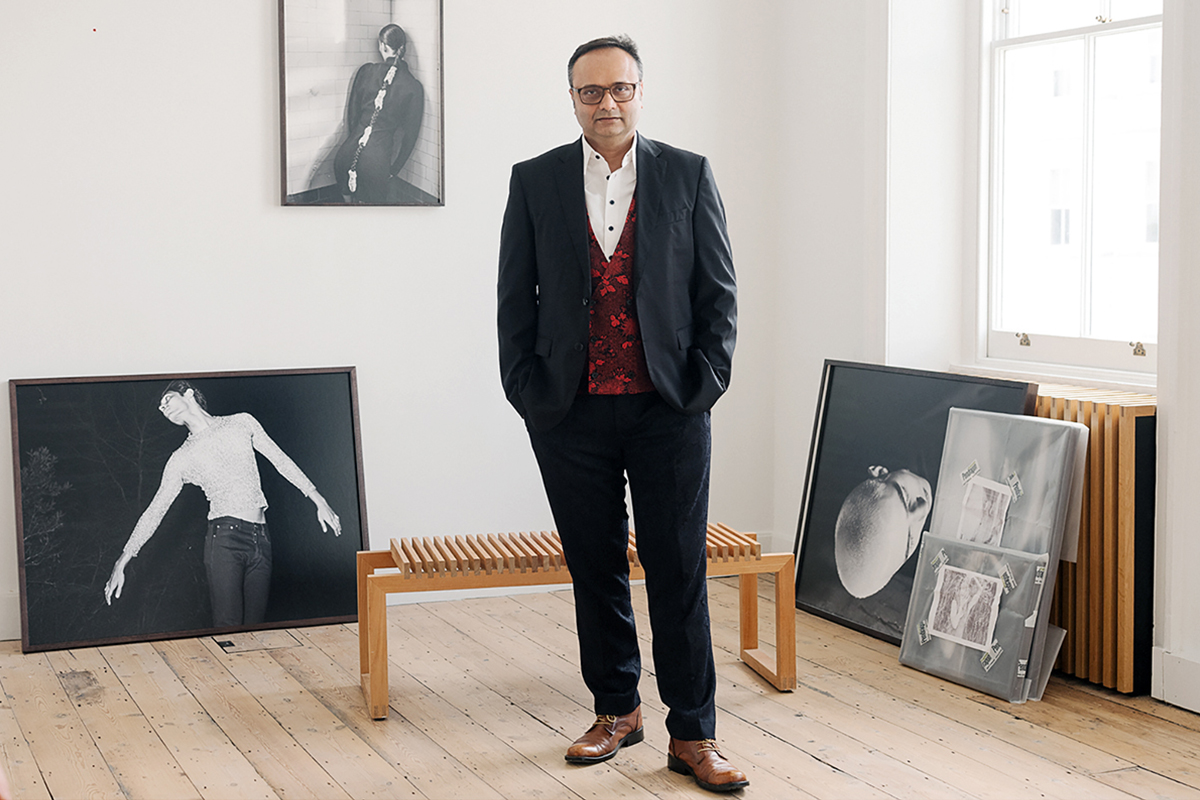

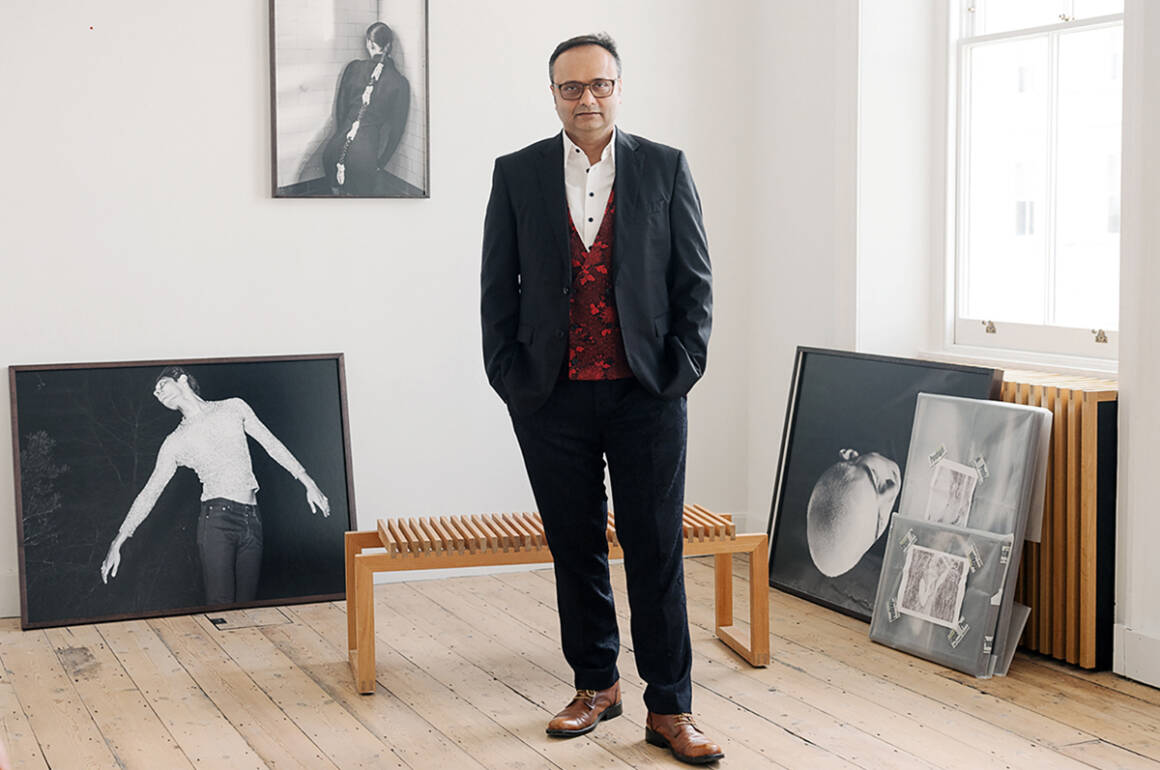
Durjoy Rahman, founder of the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation
A philanthropic foundation from Bangladesh is creating powerful ties between art and culture in East and West, with a nexus in Italy. Greg Thomas reports on the remarkable dialogues and cross-fertilisation across the Global South and North being catalysed by the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation.
“We have craft traditions in Bengal that are thousands of years old,” Durjoy Rahman tells me from his home in Dhaka, the capital of his native Bangladesh, which is part of the wider Bengal region. A vibrant abstract painting hangs on the wall behind him, and coloured beads adorn his wrist. Since launching the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation (DBF) in 2018, the art collector and philanthropist has made it his mission to promote the creative culture of his home country and the wider South Asian region, including Pakistan, India and Sri Lanka; and to create links between the Global South and North.
Over the past five years, DBF, which grew out of Durjoy’s collecting, has supported countless creatives through residencies, exhibitions and exchange programmes. It has linked up artists, art writers and craftspeople in South Asia and Europe, but also reaching across South America, Africa and elsewhere.
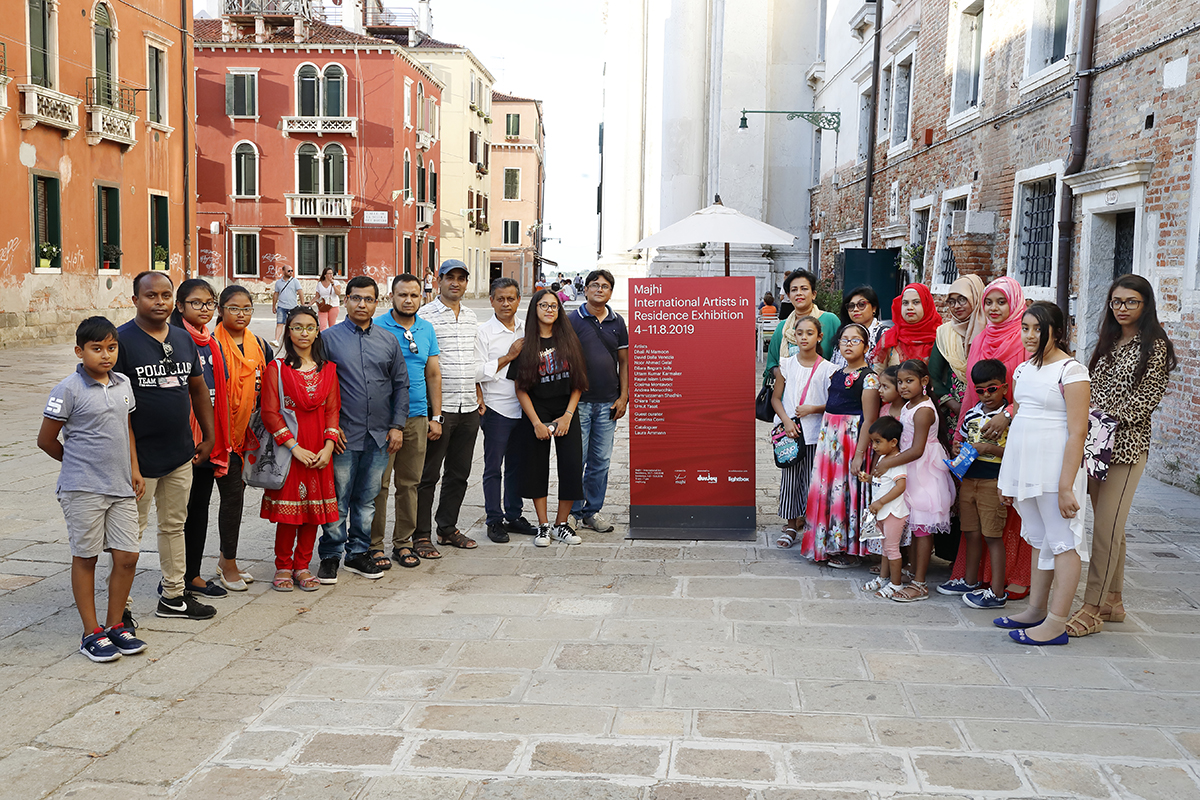

Members of the Venice Bangladeshi community, from the local Bangla language school, at an open studio visit, Majhi International Art Residency, Venice, 2019
A particular concern has always been to establish ties with Italy. Or rather, as Durjoy puts it, “not Italy, but Venice. When we were making plans to build bridges between East and West, and to think about how creative people from South Asia could gain greater visibility, we felt that Venice was a perfect place to focus our efforts. Because of the Venice Biennale, it’s a gathering point for global art populations.”
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
The foundation’s latest project, the DBF-KMB Award, was launched in Venice in 2022 in collaboration with London’s Hayward Gallery. Every two years until 2028, curators from the Hayward, with representatives from the DBF and the Kochi Biennale Foundation, will select one outstanding South Asian artist exhibiting at the Kochi-Muziris Biennale in Kerala, to show their work at the prestigious London gallery’s HENI Project Space.
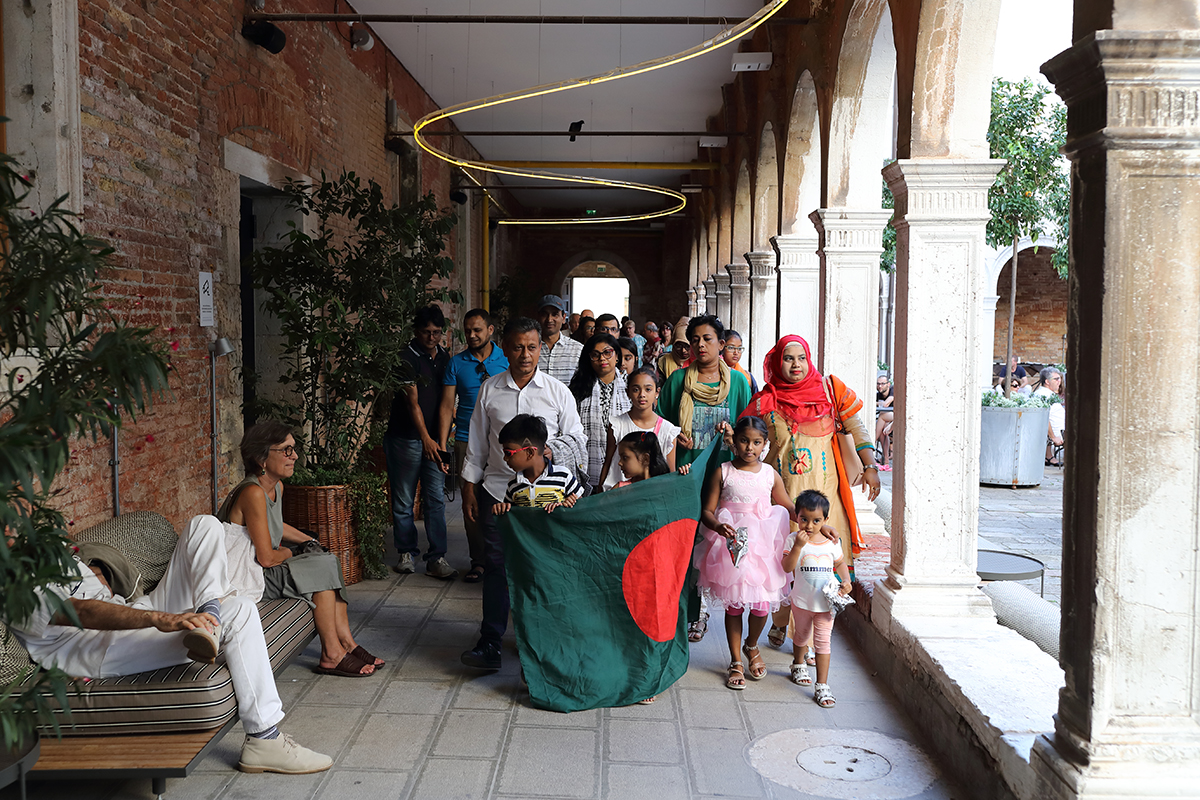

Members of the Venice Bangladeshi community, from the local Bangla language school, at an open studio visit, Majhi International Art Residency, Venice, 2019
The recipient of this year’s inaugural award was announced in Venice (of course) in July – creating the third side of an international triangle between South Asia, London and Venice. Amol K Patil is an artist who works with a variety of media including installations, drawings, sculptures and moving images. He was chosen for the award on the basis of his work at the Kochi-Muziris Biennale, an installation entitled The Politics of Skin and Movement; his work at the Hayward this autumn is a development of this theme. Durjoy says he admires Patil’s work for “seeking to bridge the gap between East and West, fostering an atmosphere of openness and embracing diversity.” Amol K Patil is also being supported by the DBF for his fellowship at the Rijksakademie in Amsterdam for a year from September 2023.
To complement the artist award and exhibition, in alternate years, an instalment of the Durjoy Bangladesh Lecture Series, co-curated by the Kochi-Muziris Biennale Foundation and programmed by Hayward Director Ralph Rugoff, will be held at the Hayward Gallery, introducing key themes and figures from South Asian art.

Arlecchino, Arlecchino and Mating Tigers, 2021, by Shezad Dawood, and Man in Shower, Porter Series, 2006, by William Kentridge, at the DBF Creative Studio, Dhaka
Durjoy often talks about his foundation’s work in terms of building bridges within and between countries. Indeed, references to water and crossings punctuate his discussion of DBF’s mission. Of equal and related significance are the affinities Durjoy sees between Bangladesh, with its maritime infrastructure and shipbuilding traditions, and the host city of the world’s most celebrated Biennale.
After all, Venice has an equally strong history of nautical trade and technology. And the businessman points out that it also has a “very large Bangladeshi community, because of the big dockyard industry. There are a lot of migrant professionals there: engineers, draughtsmen.” It is notable that, perhaps unlike some philanthropists in privileged positions in parts of the Global South, Durjoy considers all of his compatriots as equally important citizens.
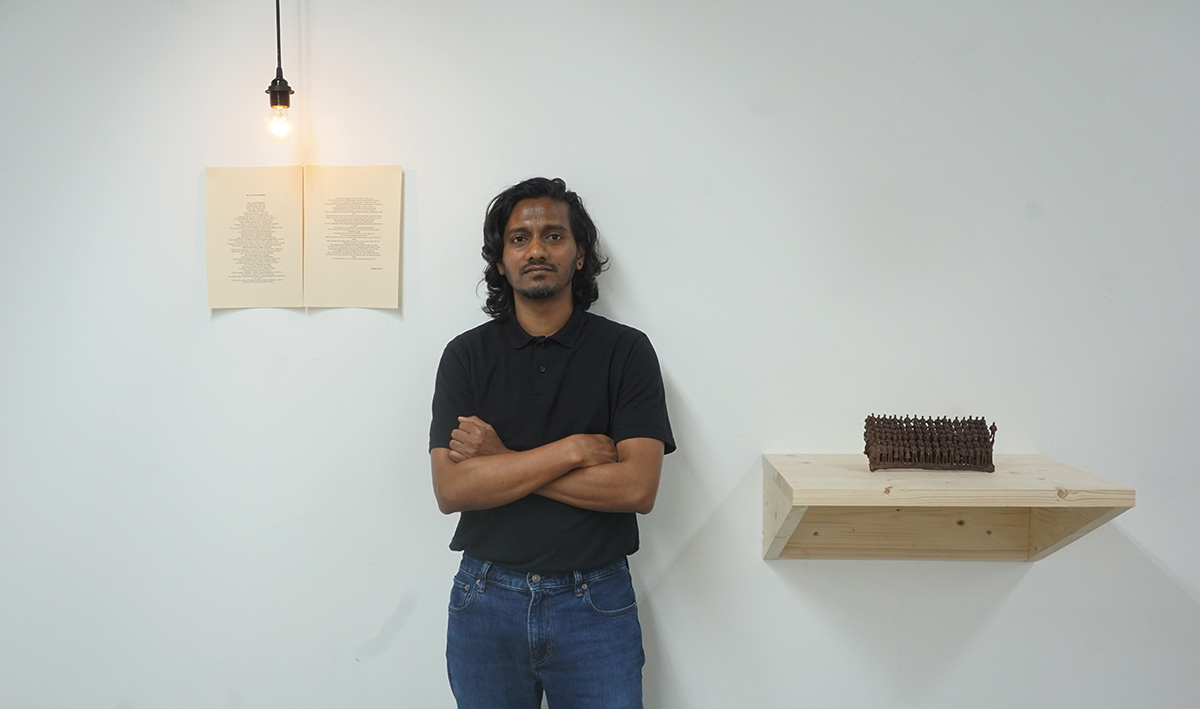

Amol K Patil, recipient of the inaugural Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation – Kochi-Muziris Biennale Award, 2023
In 2019, Durjoy launched DBF’s first major initiative, the Majhi International Art Residency Programme, hosted at Combo, a former convent in Cannaregio, Venice. This saw Venetian and Bangladeshi artists come together over two weeks to create collaborative artworks, present and perform. “The word Majhi means ‘ferryman’,” says Durjoy. “In Venice they have gondolas on their canals and in Bangladesh we have many boats on our waterways, too, so it makes sense. ‘Majhi’ also means ‘leader of the house’ or ‘leader of a group of people’, and I’d like the scheme to show a possible future direction for artistic endeavours in Europe.”
Majhi 2019 was also about nurturing local Venetian talent. Participant Andrea Morucchio is a Venetian artist whose practice raises awareness of the impact of mass tourism in Venice. His Covid 19-era project, Venezia Anno Zero, documented the serenity of La Serenissima during lockdown. “And we didn’t work in isolation from the Venetian Bangladeshi community, either,” Durjoy continues. “There’s a school that teaches Bengali to the Bangladeshi children in Venice, and the children came to see a performance by an artist from Bangladesh.”
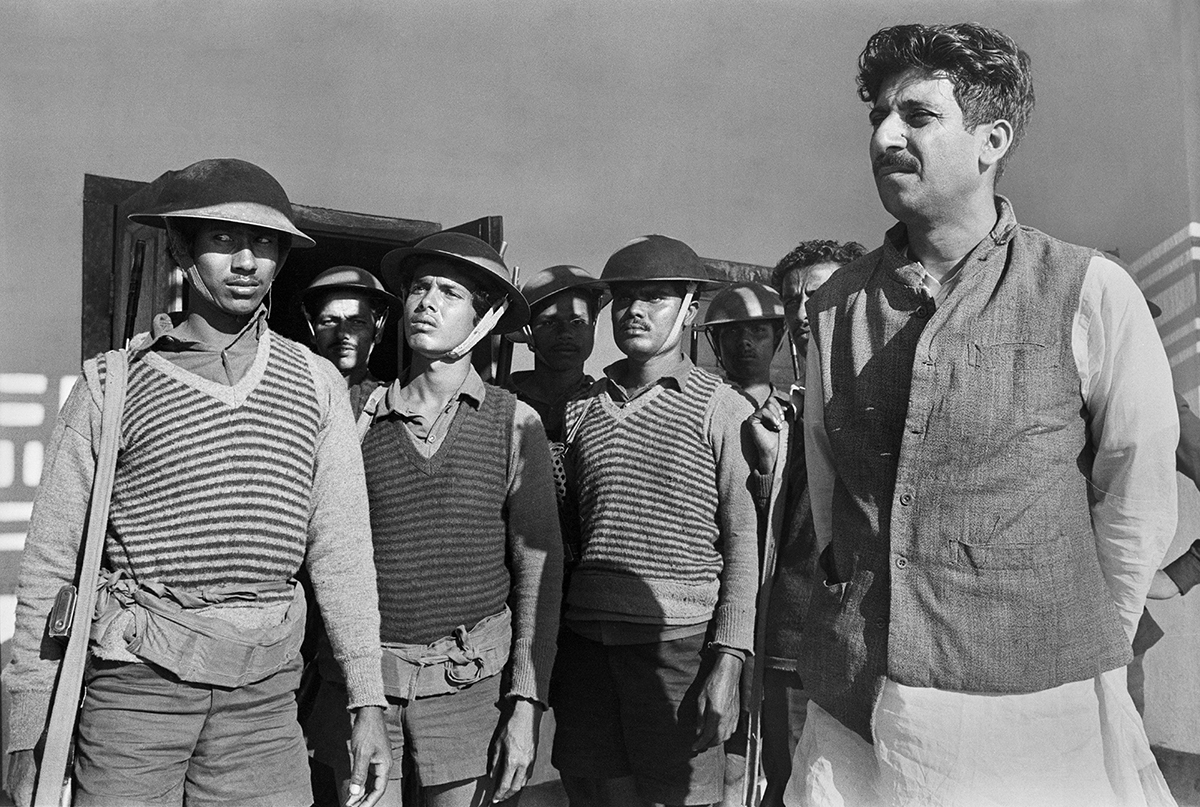

Sheikh Abu Naser, freedom fighter and younger brother of “Bangabandhu” Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, on the battlefield, 1971, by Raghu Rai, DBF Collection
Subsequent Majhi projects have also strengthened DBF’s connections with other European countries and institutions. DBF has a strong presence in Berlin, which made it possible to host the second Majhi Art Residency in Berlin in 2020 during Art Berlin, immediately before Berlin went into lockdown. In fact, DBF’s first collaboration, in 2018, was with German museum the Kunstmuseum Wolfsburg, to which Durjoy donated a major installation by Mithu Sen, the first work by a female Indian artist collected by a major German institution. The third Majhi residency was held in 2021 in Eindhoven, another city where the foundation has a strong presence.
A further recent major achievement of the foundation was the creation of the DBF Creative Studio. This former storage unit of Durjoy’s was converted into a gallery and space for limited gatherings during lockdown, as a way of exhibiting the wonders of the DBF collection in a safe setting.
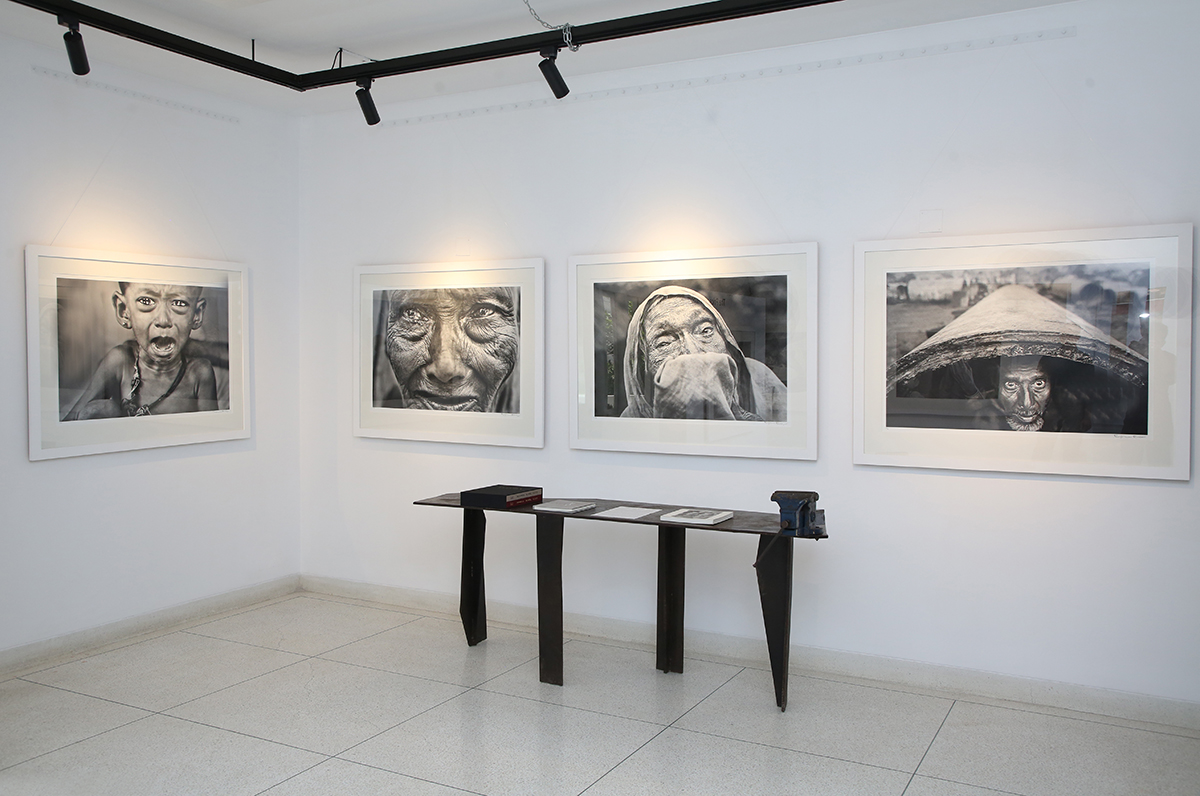

Photographs from the 1971 Bangladesh liberation war, from the book Rise of a Nation, by Raghu Rai, images from the DBF Collection, shown at the DBF Creative Studio
Through it all, connections to Venice have remained central. In October 2019, following the first Majhi residency, artists involved in the scheme came to Dhaka to take part in the city’s first Italian Contemporary Art Days, supported by the Italian Embassy in Bangladesh and other partners. This was part of the wider programme for the 15th Italian Contemporary Art Day and “a prime example of how a cultural bridge can cross borders,” Durjoy notes. Meanwhile, in Dhaka, the Durjoy Bangladesh Foundation works closely with the Italian Embassy in other areas – notably staging a vintage car and motorbike event to celebrate 50 years of friendship between the two countries last year.
Read more: Art Dubai opens in support of South Asian artists
What is the wider context for DBF’s work? The idea of “writing back to the centre” is a common trope in postcolonial literature and theory. “Writing back” identifies a paradigm wherein liberated nations turn the tables on the cultures of their former colonisers through the critical optic of art and writing.
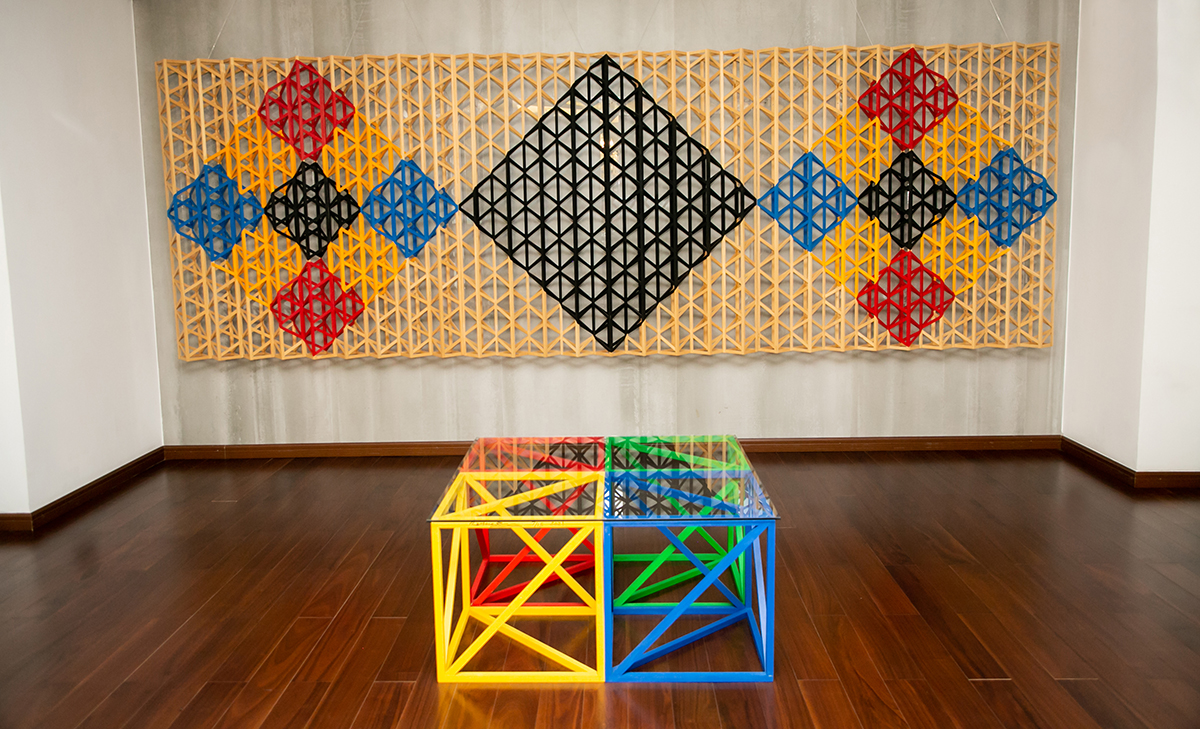

Black Square Breaking into Primary Colours, 2016, by Rasheed Araeen, DBF Collection
A similar idea underpins Durjoy’s thinking on DBF’s work, which is not just about building bridges but also about subverting what he calls “the Western gaze” on South Asian culture. “It’s not about blaming anyone,” he clarifies. “It’s just that when publications about South Asian art appear, the scholars have all been groomed within the Western education system, so you get a European or American perspective.” Within news culture, meanwhile, the Western gaze has been predisposed to find images of disaster and deprivation, particularly since the 1970s, when independence from Pakistan in 1971 was followed by a period of famine and hardship for much of Bangladesh’s population.

Enrico Nunziata, Durjoy Rahman, Atiqul Islam, Shahriar Alam and Anjan Chowdhury, at the opening of the DBF/Italian Embassy vintage car and motorbike event, Dhaka, 2022
Durjoy doesn’t seek to counter negative tropes within uncritically positive ones. In fact, he is keen to talk about how the British Raj and latterly the government of Pakistan – which took control of what is now Bangladesh, first as East Bengal and later as East Pakistan, after the 1947 partition of India – both subjugated national creative cultures. “It’s not only colonialism but achieving independence late, in 1971, that has hindered the cultural development of Bangladesh,” he reflects. “And the loss of connection with our cultural heritage was due to these same factors. During colonial times, craft and creative endeavours were purposely obstructed so that craftsmen could get on with work more useful to the colonial government. Then, after the 1947 partition, still other aspects of our cultural heritage started fading away, including our own language, Bengali. There was a revolution in 1952 to protect the language.”
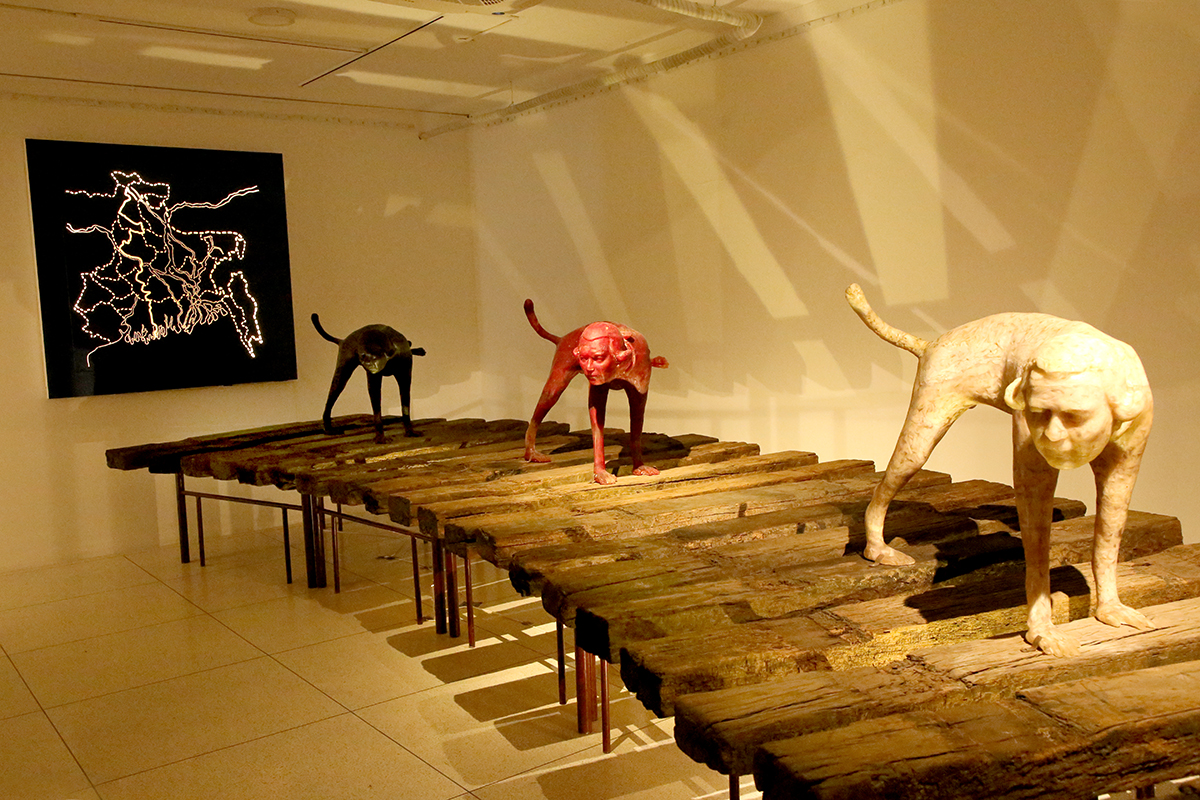

History/Cartography/Territorialism, 2023, by Dhali Al Mamoon, participant in the Majhi International Art Residency in Venice, shown at the DBF Creative Studio
Happily, many of these traditions have been reborn in recent decades, with Bangladesh’s millennia-old textile industry an area of growth, notably through renewed production of jamdani, a fine handspun muslin cloth that has become an emblem of national cultural pride.
Nonetheless, as Durjoy points out, DBF’s programme for his country’s ongoing cultural rejuvenation remains timely and relevant in a global arts scene seeking to heal rifts caused by imperialism. As Durjoy puts it, in a phrase that is reminiscent of that ferryman again, the foundation is “on time”. All aboard for the ride, from Dhaka to Venice, London and elsewhere.
Read more: durjoybangladeshfoundation.org
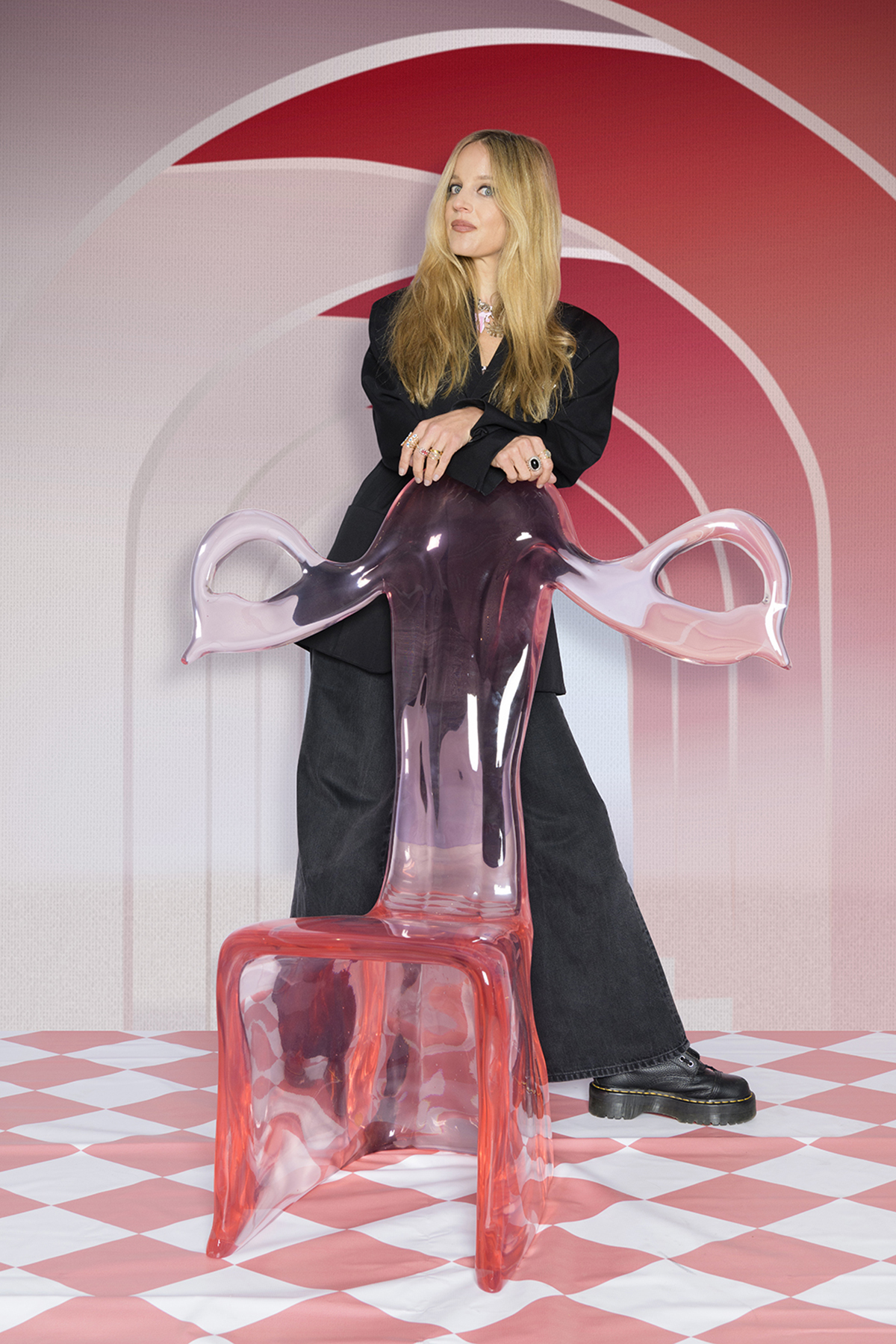


































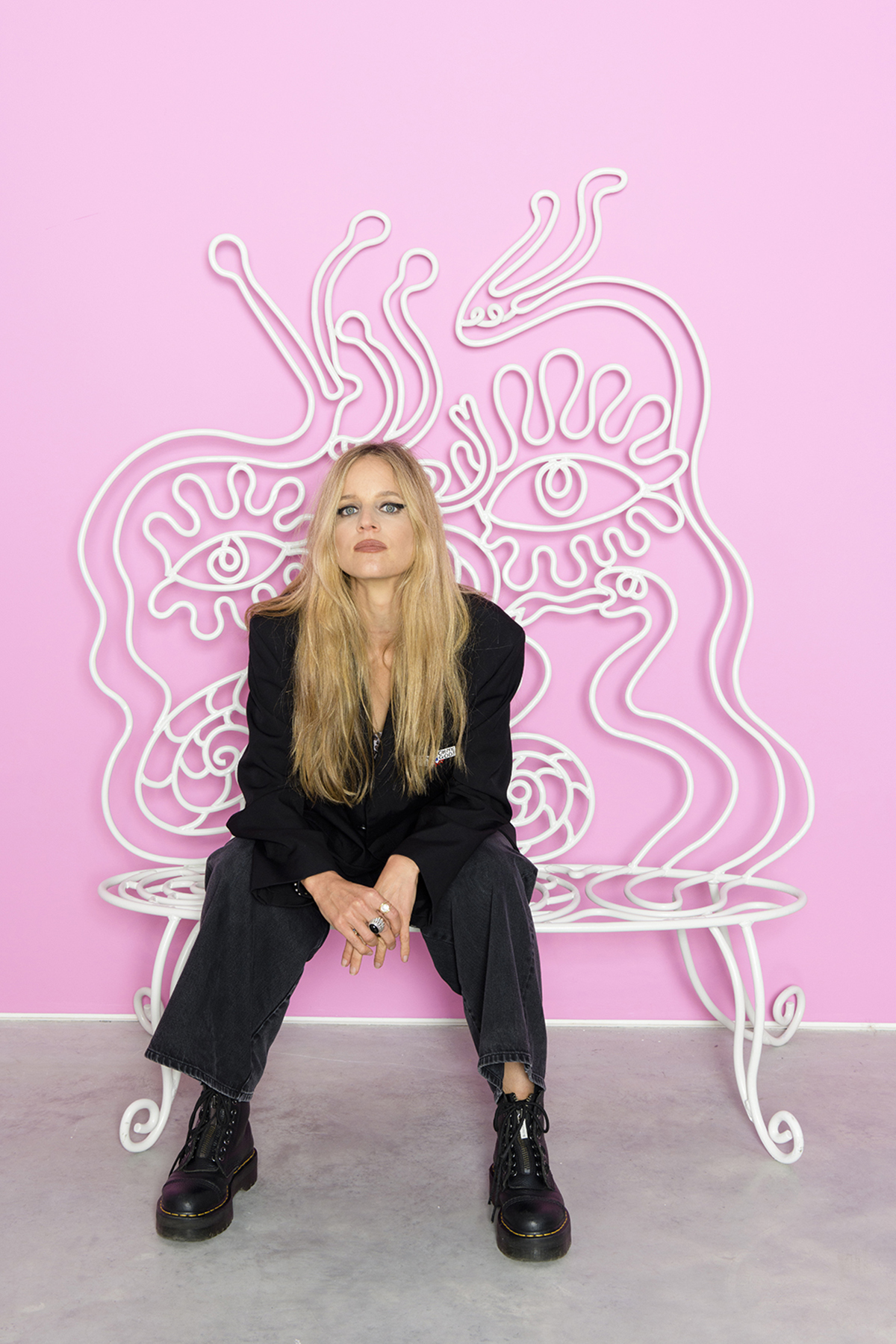
 Filmmaker and artist Charlotte Colbert’s latest exhibition, “Dreamland Sirens,” is set to take over Fitzrovia Chapel in Pearson Square. The show curated by Simon de Pury, marks UTA Artist Space’s London debut under the leadership of Zuzanna Ciolek
Filmmaker and artist Charlotte Colbert’s latest exhibition, “Dreamland Sirens,” is set to take over Fitzrovia Chapel in Pearson Square. The show curated by Simon de Pury, marks UTA Artist Space’s London debut under the leadership of Zuzanna Ciolek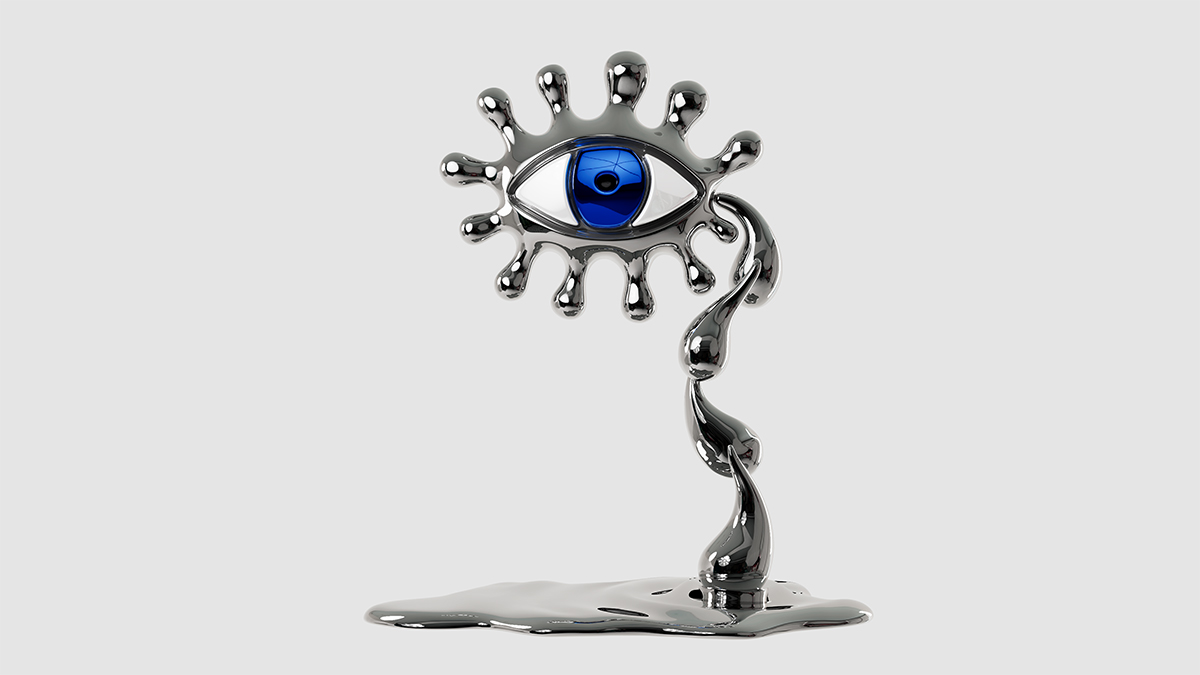








































Recent Comments