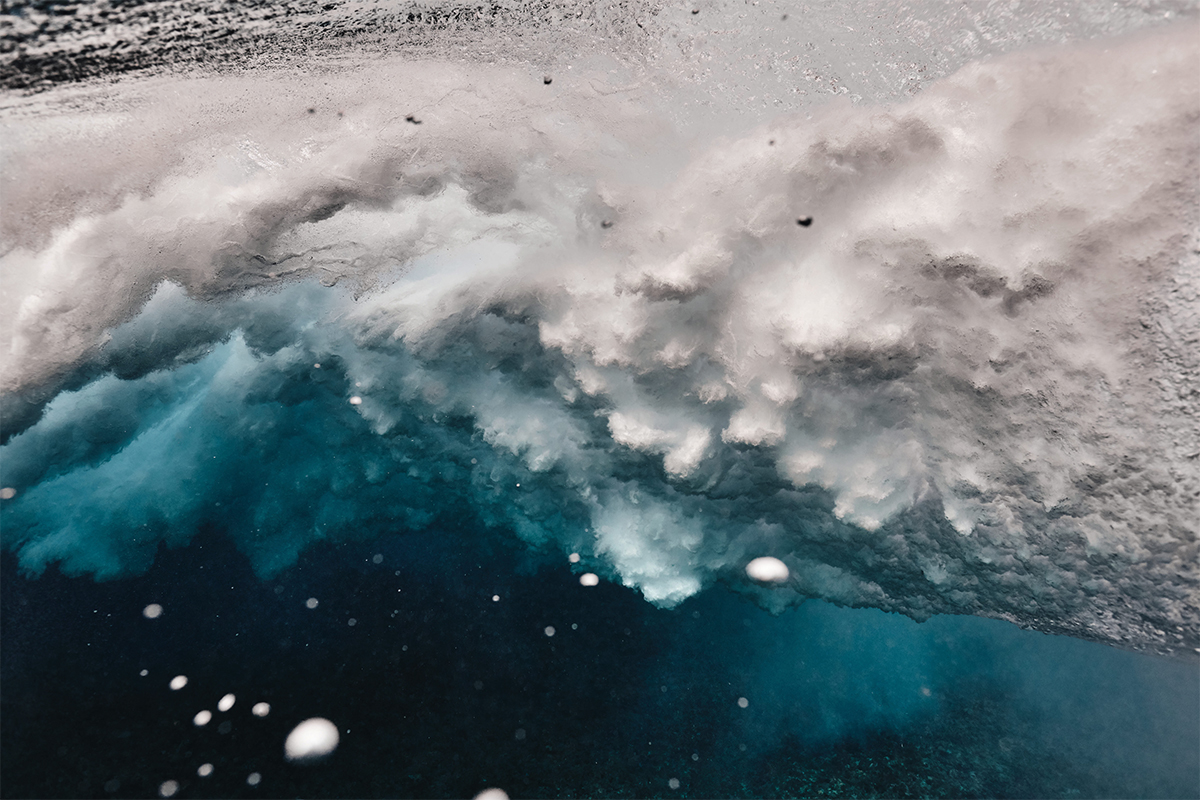

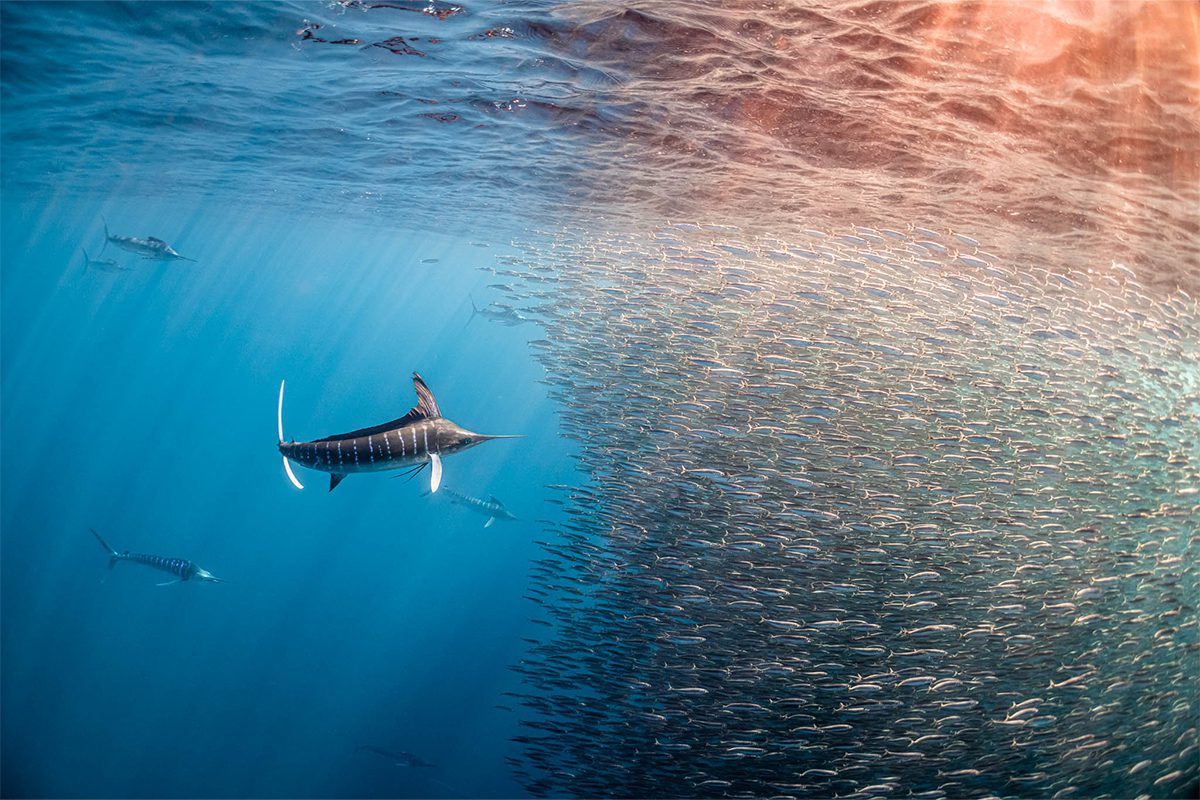
Marine biologist Matt Sharp was awarded the Ocean Conservation Photographer of the Year in 2020 for his incredible images, such as this one of a wave breaking in the Maldives in 2019
Marine life is threatened by climate change, pollution and overfishing. And depleted oceans risk collapsing the whole global ecosystem. A new generation of business startups is aiming to reshape the ocean economy, making it both truly sustainable and profitable. Michael Marshall reports
The blue economy is gaining momentum. Hundreds of startup companies around the world are aiming to protect, and even restore, the oceans, while making a profit. They want to get food and other essential resources from the sea in ways that benefit marine life – or at least don’t harm it. What’s more, there are plenty of organisations that aim to support these startups, whether with money or expertise or both.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
“We are not going to save the oceans if we don’t change the economy,” says Tiago Pitta e Cunha, the CEO of the Oceano Azul Foundation, a Portuguese non-profit that supports a variety of initiatives designed to stimulate the growth of the sustainable blue economy. The good news is that the business case for ocean conservation is real and growing. “There’s a wonderful opportunity for startups and new companies to develop business models,” says John Virdin, director of the Oceans & Coastal Policy Programme at Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment in Durham, North Carolina.
The ocean certainly needs our help. It faces three big problems – overfishing, pollution and climate change – that “tend to make each other worse”, says Nancy Knowlton, a professor of marine biology and Sant Chair in Marine Sciences at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. However, she adds, there have been some real success stories for ocean conservationists in recent years. Take Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), for example. These are regions of the ocean in which extractive industries are either banned or tightly regulated, and they have proven highly beneficial when implemented fully. In 2020, fully implemented MPAs covered 5.3 per cent of the ocean, and this area is growing every year. As a result, some animals that were once considered on the brink of extinction have increased in numbers, including many whale species.
At the moment, the blue economy is dominated by “a few really big fish”, Virdin points out. In 2021, he co-authored a study that found 60 per cent of all revenues obtained from the ocean came from just 100 companies, almost half of which were from the oil and gas industry. Such companies have “rigid processes in place, for good reasons”, says Alexis Grosskopf, the founder and CEO of OceanHub Africa in Cape Town, South Africa, an accelerator for ocean impact startups. Those processes “could not be disrupted smoothly and quickly enough, without blowing up or imploding”.
This is where startup companies come in. Small outfits with radical technologies and new ways of doing things can overthrow existing practices, if they’re successful enough. And in the blue economy there are now hundreds aiming to disrupt a variety of industries, from fishing and aquaculture to renewable energy, pharmaceuticals and waste management. Some want to take an existing industry, such as fishing, and do it better, causing less harm to the ocean ecosystem. Others are aiming to restore and repair, actively improving the marine environment while also making a profit.
As with all startups, the challenge is to survive long enough to build a customer base and break even. A startup company may attract an initial burst of funding on the basis of a good idea, which enables it to start operations. But they then face ‘death valley’, when they risk running out of money before they start earning any.
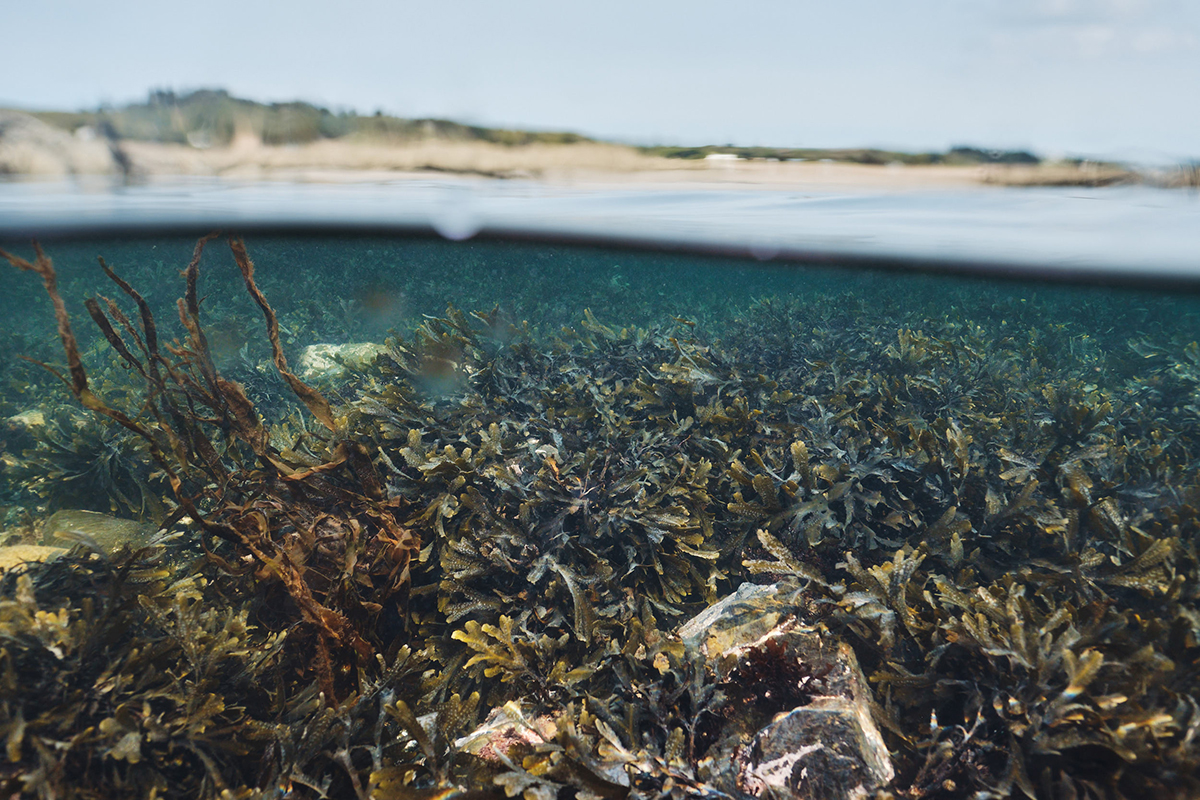

Intertidal seaweed beds on the west coast of Jersey, UK, in 2020
To address this challenge, a number of incubators and accelerators have been established in recent years to help ocean startups become profitable. These include Katapult Ocean in Oslo, Norway and OceanHub Africa in Cape Town, South Africa. Another is Blue Bio Value, which was set up by the Oceano Azul Foundation and the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation in 2018 to “help entrepreneurs create commercially viable and sustainable businesses” and thereby “accelerate the transition to a global and sustainable blue bioeconomy”. It is now on its fish set of startups.
Previously, the Oceano Azul Foundation – which owns the Lisbon Oceanarium – had focused on ocean education, but its leaders decided this was not enough. “We thought that, as a credible foundation, we need to also put our money where our mouth is,” says Pitta e Cunha. “We only accept startups that, through their production, will ease decarbonisation of the planet or high consumption of natural resources.” Many of these startups are led by scientists, he explains, who have essential specialist knowledge but little experience of markets or running businesses.
Alongside the accelerator, the team has also created an ideation programme to link academic researchers and business leaders, to encourage the formation of new businesses. “We are trying to manufacture new startups, because they are needed,” Pitta e Cunha says.
With so many funders, incubators and accelerators entering the ocean economy, the challenge for the owners of a new startup is how to navigate this business world. Several organisations have now been set up to organise everything and help startups find their way.
At Investable Oceans, in New York, the co-founder and principle, Ted Janulis, likes to say he was “born with an ocean gene”, which means he “can’t walk past a body of water of any type without jumping in and splashing around”. Several decades in finance convinced him that there were market-based opportunities all over the ocean economy. But the investors were scattered and disconnected. “The people who invested in plastic mitigation weren’t necessarily the people investing in better fisheries or aquaculture,” he says. So he set out to create a single platform where people could come and learn about investment opportunities in the blue economy across all asset classes and sectors. “We’re not an incubator, we’re not an accelerator, we’re not a fund and we’re not a broker dealer,” he says. “Our goal is to connect people.”
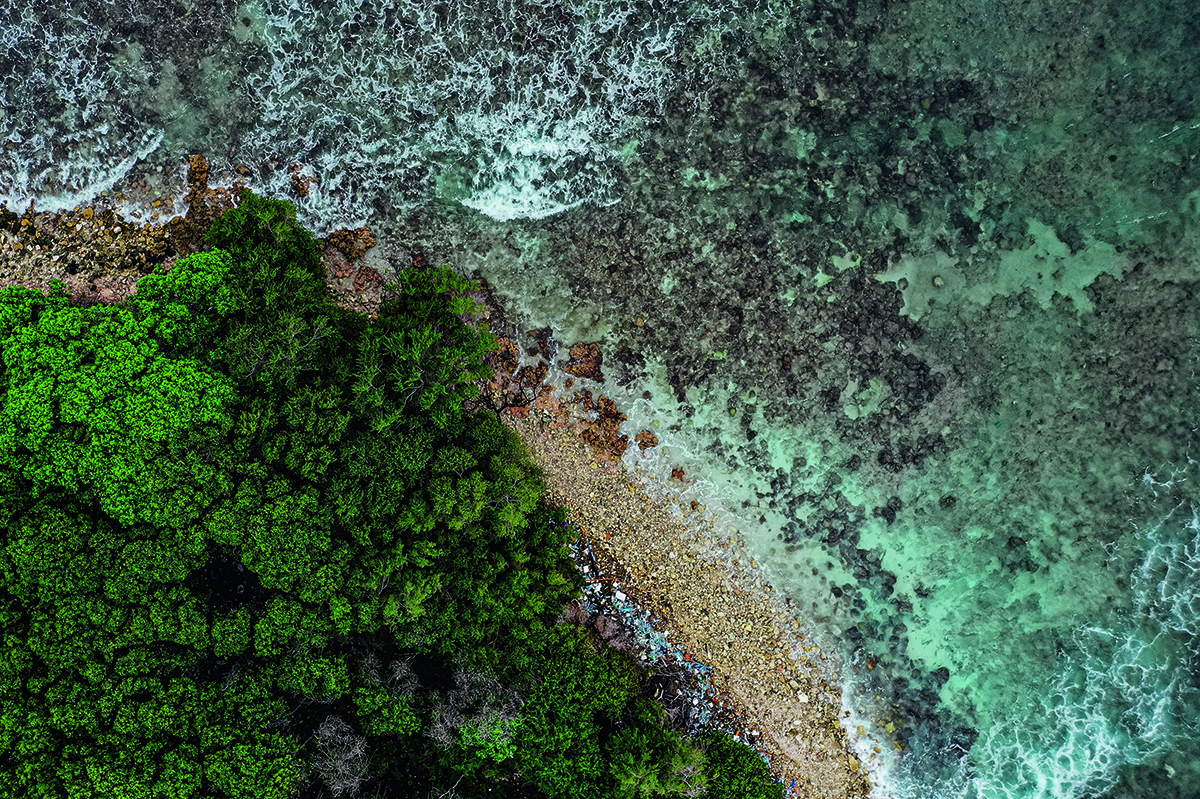

Plastic pollution along the beach– knee-deep in some places – in the Maldives in 2019
More recently, an umbrella organisation called 1000 Ocean Startups was launched in May 2021 to accelerate ocean impact innovation by bringing together “incubators, accelerators, competitions, matching platforms and VCs supporting startups for ocean impact”. Its members include Katapult Ocean, OceanHub Africa and Investable Oceans and so far it has backed 168 startups: 115 focused on sustainable use of ocean resources, 33 addressing pollution and 20 tackling climate change. “We’re still in the infancy stage,” says Grosskopf. The aim is to back 1,000 startups by 2030.
The challenge for all these companies will be to compete against existing ocean businesses that are not making efforts to be sustainable, and therefore have lower operating costs. Some consumers are prepared to pay extra for sustainable products, but many will not or cannot, so the startups must compete on price to attract mass-market consumers.
Fortunately, there are many routes to success, says Janulis. “Some of it might be that it’s a standalone company that becomes really big,” he says, but startups can also be absorbed by larger companies that see their methods as an opportunity.
Janulis says there is also “a rising sensibility and more awareness”, a point echoed by many. “I was born as a digital native,” says Grosskopf. People from the generation below, he says, are “sustainable natives”. “The consumers of tomorrow, the employers of tomorrow… they have sustainability in their DNA.”
It will soon be impossible for companies to behave unsustainably, Virdin suggests. “These issues of sustainability of ocean ecosystems and communities, they’re not luxury issues,” he says. “These are core issues to the future of the business model, whether it’s social licence to operate or whether it’s risks to your operating environment in the coming decades.”
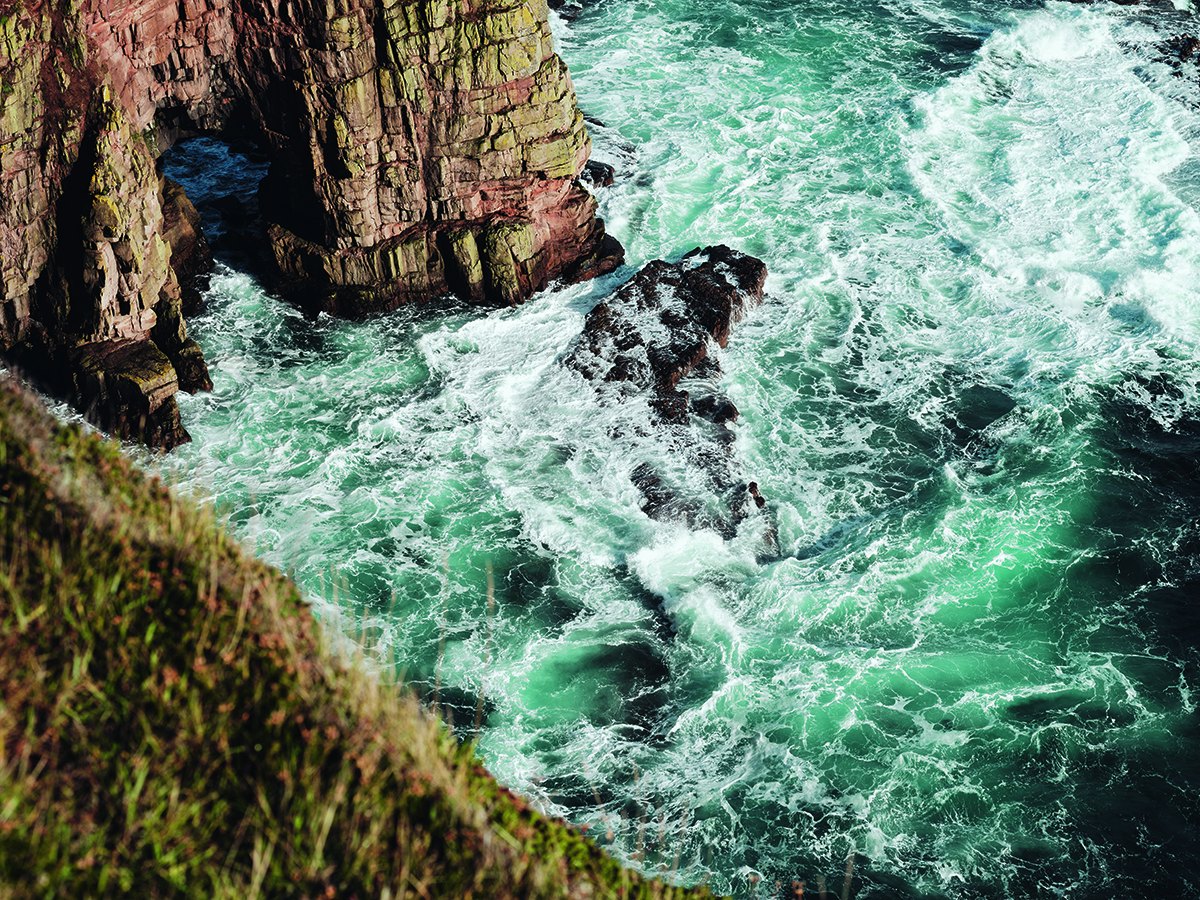

Duncansby Stacks last year, on the exposed north- east coast of Scotland, where seals and seabirds thrive
Knowlton cautions that it’s unlikely startups alone can fix the marine environmental crisis. “The problem is that we’re kind of in a race against time,” she says, so there will need to be top-down action as well. “The role of government is really important because it can motivate change quickly.” However, she acknowledges, startups are where creative ideas can be brought to fruition quickly. “I think you have to encourage entrepreneurship – and much of it will fail, but some of it will work.”
Read More: Kering’s Marie-Claire Daveu on benefits of the blue economy
In other words, it’s not a choice between buccaneering startups and rules-based government. To save our ocean, both will have to work together.
Savvy Ocean Startups
Pesky Fish: Many of the fish that are caught at sea, particularly by trawlers, are wasted. Because they aren’t fashionable, they are discarded as ‘bycatch’. The British company Pesky Fish aims to change that by allowing fishers to sell directly to consumers. It has a rapidly updated online shop and overnight delivery service.
Recyglo: Plastic waste is one of the biggest problems facing the ocean ecosystem. Today most plastic enters the ocean from east Asia, where waste management systems are poor. Recyglo is aiming to change that by bringing modern recycling to the region. It already has branches in Myanmar, Singapore and Malaysia.
Cascadia Seaweed: Farming seaweed has enormous potential to feed the growing human population, remove carbon dioxide from the air, and restore the ocean by providing habitat for marine animals. Canadian firm Cascadia Seaweed is turning kelp into food for people and farm animals. It is working in partnership with First Nations groups.
This article appears in the Deutsche Bank Supplement of the Summer 2022 issue of LUX




































































Recent Comments