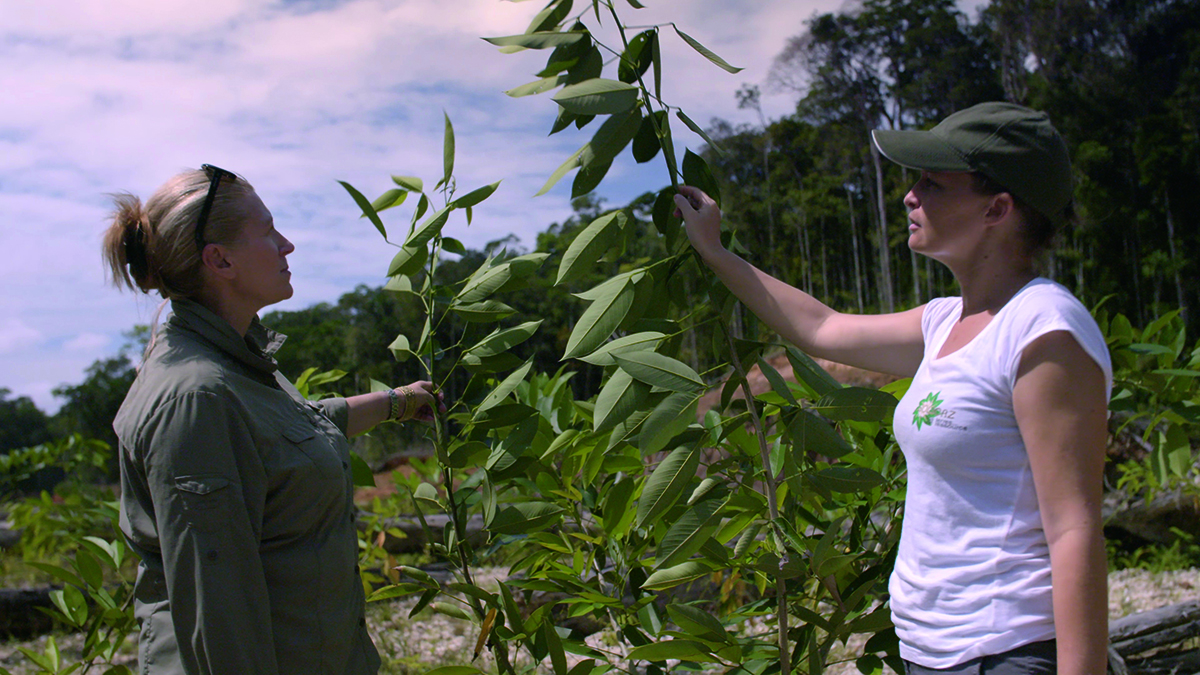

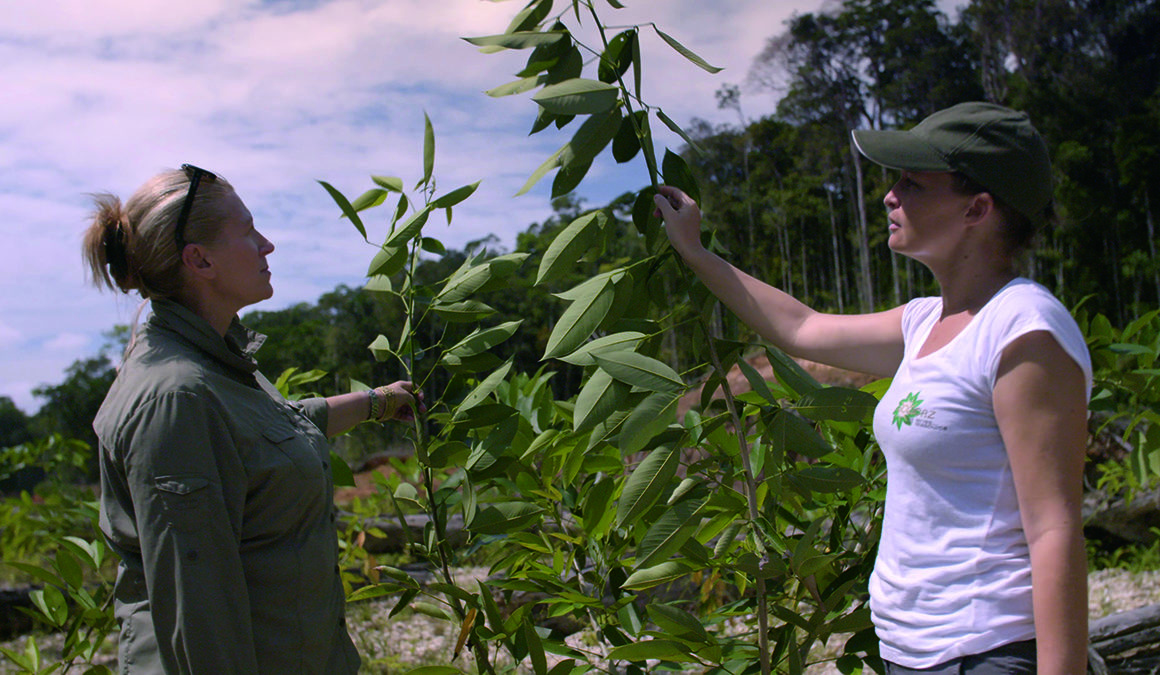
Marie-Claire Daveu with Elodie Brunstein of ecological engineers Solicaz in French Guiana. Image by Magneto.
The Kering group, owner of Gucci and Bottega Veneta, led the luxury industry by pioneering a sustainability strategy years ago. Marie-Claire Daveu, who spearheaded this move, explains how environmental accounting and the blue economy are good for business, consumers and the planet
DEUTSCHE BANK WEALTH MANAGEMENT x LUX

Marie-Claire Daveu. © Benoît Peverelli
The fashion industry is dependent upon nature’s resources to manufacture. It is also a vast industry and, unfortunately, one of the most polluting. This means we have a specific responsibility to act now and transform our business model to mitigate the diminution of resources, loss of biodiversity and climate change that we already see affecting our industry and our planet. Sustainability is not an option; it is a necessity. And it demands definitive action from the fashion industry and beyond.
The blue economy in particular has to be a huge focus for everyone. The oceans are the lungs of the Earth, producing more than half the world’s oxygen and helping regulate our weather. But in the past few hundred years they have absorbed vast amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas emissions, raising their temperature and changing their chemistry and ecosystems. Marine animals and humans rely on the oceans to live, and the only way to mitigate the harm being done is to change the way we operate here on land – from reducing plastic and chemical waste to choosing renewable energy sources where possible.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
Kering has already implemented a series of measures specifically in recognition of the rapidly degrading ocean environment. We have been working for years to preserve ocean biodiversity via programmes and partnerships with recognised associations – most recently, the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). And in 2017, our chairman and CEO, François-Henri Pinault, presented the Fashion Pact to the G7, incorporating ocean protection as one of its main environmental goals. It proposes a set of concrete actions, such as the adoption of pollution controls to safeguard the rivers and oceans from chemicals released through the fashion production processes; and compels companies to develop innovations that will eliminate microfibre pollution from the washing of synthetic materials.
Such innovation is vital to growing a sustainable blue economy. In 2017, we committed to reducing our environmental footprint by 40 per cent by 2025, and half of that reduction will come from innovation, which is crucial if we want to bring new solutions into our business model.
Today, we are looking for and investing in innovations that can address blue economy challenges, including closed-loop recycling, alternative materials and sustainable sourcing. But there is still a long way to go. One of the main challenges the blue economy is facing is plastic, used to pack, transport and store garments. The fashion industry needs to urgently tackle polybag-packaging waste. One possible innovation has been developed by the Plastics Packaging Project – a Fashion for Good initiative supported by a coalition of companies, including Kering. The project aims to reduce the impact and use of plastic packaging, and recently launched a pilot for the collection and recycling of garment polybags. They will be transformed into new plastic film products, closing the loop and dramatically reducing the amount of plastic waste that often ends up in our waterways.

Kering’s Materials Innovation Lab. Image by Jean-Luc Perreard
Transparency will be vital to the longevity of such initiatives. Studies show that millennials and Generation Z are very sensitive to sustainability – with a keen focus on traceability. They also have very high expectations. Generation Z entering the workforce, together with increasing sustainability questions from consumers, will drive further efforts in the fashion industry and increased transparency around a product’s origins.
Read more: These photographer-activists are capturing underwater beauty
Corporate sustainability agendas must take into account a product’s entire impact, from the raw materials to products reaching clients. At Kering, this has become an essential part of our products’ excellence, and we have made that process transparent through the creation of our Environmental Profit and Loss (EP&L) system, which measures, monetises and monitors the full environmental impact of a company’s operations across the entire supply chain, including greenhouse gas emissions, water use, water and air pollution, waste production and land use change. When you think about what is behind luxury, sustainability is often already built in: we use the highest quality raw materials; our products are made by skilled craftspeople; and some of them are passed down from generation to generation. They have to be perfect; even their sustainability must be perfect.
Building a sustainability strategy is about taking your whole supply chain and its impacts into account, and activating programmes to mitigate these impacts. The blue economy can be fully part of an environmental policy, and sustainability as a whole should be very much integrated in a company’s strategy. As an example, we know that the high-quality raw materials in luxury goods are ‘pre-designed’ for circularity, because of their value and versatility. But brands can extend product life cycles even further by employing recycled and upcycled materials. One blue-economy example within our supply chain is our collaboration with Econyl, makers of regenerated nylon yarn made of recycled fishnets, textile and industrial nylon waste. It has the same high quality as less sustainable alternatives, but can be endlessly regenerated.
Innovative collaborations such as these are the answer to accelerating sustainability. Our collaboration with IPBES is helping to strengthen the evidence base for better informed decisions about nature. And our EP&L hackathon in October 2019 brought developers and sustainability experts together to create digital tools that provide greater transparency around fashion’s footprint.
The message is clear: we want to play a pivotal role in leading the shift towards a sustainable future, but we can’t do it alone. Our action must be science-based and results-oriented. The private sector, governments and international organisations need to collaborate to protect nature and build a globally sustainable economy.
I am a very optimistic person, and I can see that a real shift has happened recently. Sustainability is at the heart of every conversation, both from companies and media, and this is a very good sign. Now it’s time for implementation, with unwavering determination. Fashion’s influence holds the key to accelerating those sustainable practices, both within our industry and beyond.
Marie-Claire Daveu is Kering’s chief sustainability officer.
Find out more: kering.com/en/sustainability
This article originally appeared in the LUX x Deutsche Bank Wealth Management Blue Economy Special in the Summer 2020 Issue.













Recent Comments