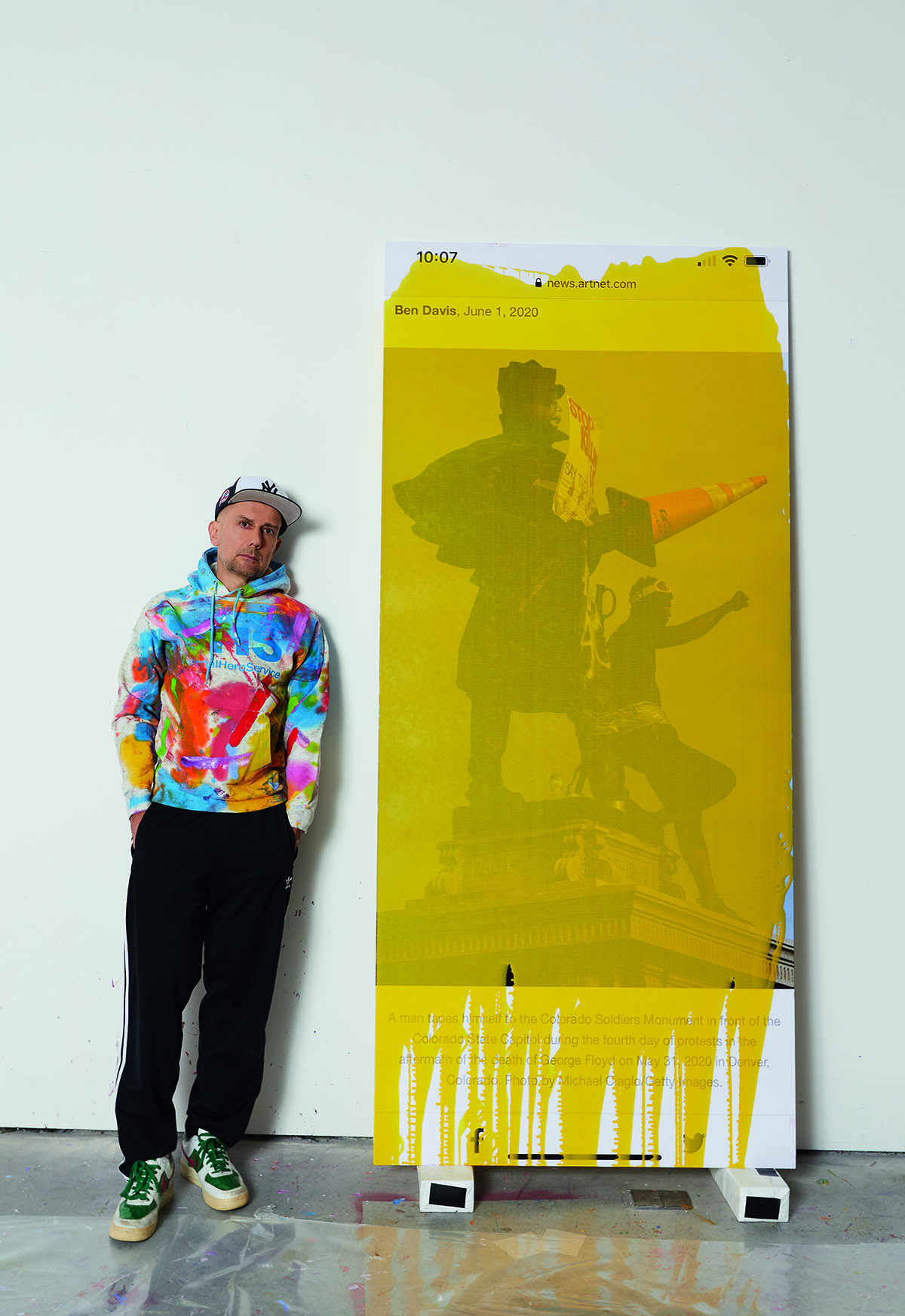
Marc Quinn in his studio with his work Viral Painting. A Man Tapes Himself to the Colorado Soldiers Monument, Artnet (2020)
From his sculpture for Trafalgar Square’s fourth plinth to his recent guerrilla monument to replace the toppled bronze of a slave trader in Bristol, British artist Marc Quinn has shown a commitment to giving form to political urgency. Maryam Eisler talks to him about his time during lockdown, his engagement with history in the making, and his renewed excitement at creating art
Maryam Eisler: Marc, tell me about your lockdown experience.
Marc Quinn: It’s totally abstract and totally real at the same time. This moment is one of the most real things we’ve lived through. There are people dying. People’s businesses are closing. Horrific things are happening. And then when you go onto the street, until very recently, there’s no-one around. It’s not like a normal war or natural disaster, where there is visible chaos. This experience is quite abstract. In the end, apart from the people who are near me, the only way I know about what is going on in the world is via my phone and the internet.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
This time has also been about a completely new way of thinking. We have been forced to learn how to navigate the difference between our virtual selves and our real selves.
In terms of making work, it’s been great. It’s me, alone in the studio making things. It’s like going back to square one again and rediscovering my roots. It’s about making art in a way that I used to do 25 years ago. And I really enjoy it.
It’s a great time for transformation. People are actually engaging with the world. There has been a whole resurgence of the Black Lives Matter movement after the horrific death of George Floyd. That is amazing, and hopefully something lasting will come from it this time around. We’ve had moments of focus on these types of issues before but never to this extent. I think it’s a time when societal tectonic plates are shifting. Our old life is also shifting.

Viral Painting. If You Are Neutral in Situations of Injustice You Have Chosen the Side of the Oppressor, Marc Quinn, 2020. Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio
Maryam Eisler: Tell me about your series History Painting and how it has led to the new series Viral Paintings. How are they made?
Marc Quinn: History Painting is a series of paintings that I have been quietly working on for about ten years. The history of art tells you about how art was classified in the 18th and the 19th centuries, with the lowest genres being portraiture or still-life and the highest being history painting. Works in that genre were commissioned by the state or by the aristocracy. When I saw images taken during riots, such as in London following the death of Mark Duggan in 2011, I thought to myself that this is actually quite interesting because the genre is being flipped on its head. History is now being made from the bottom up, coming from the people instead of the other way around. I thought I could take this idea behind the history painting genre and make new history paintings that are about the day, the moment.
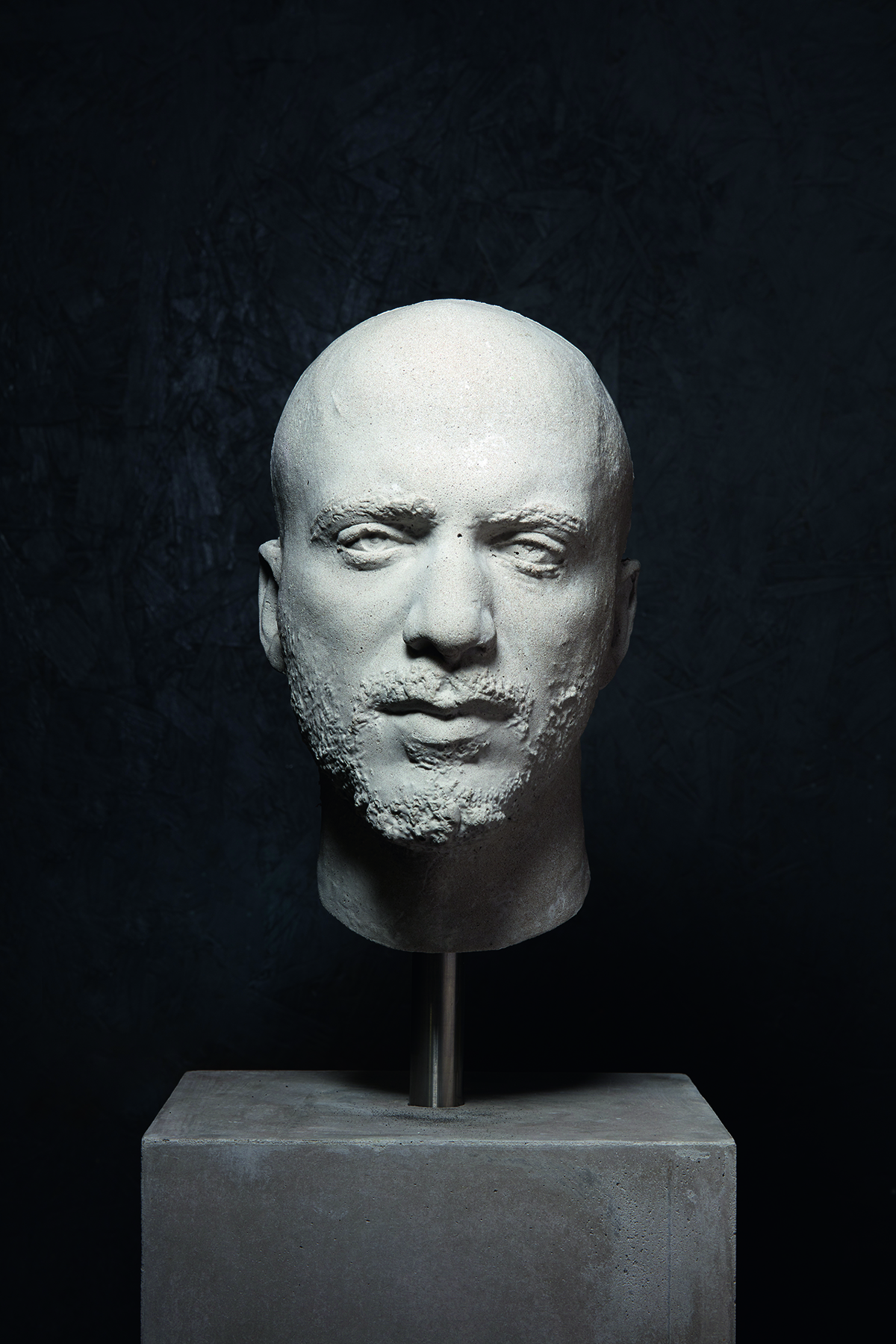

Hassan Akkad (2020) from the series 100 Heads. Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio
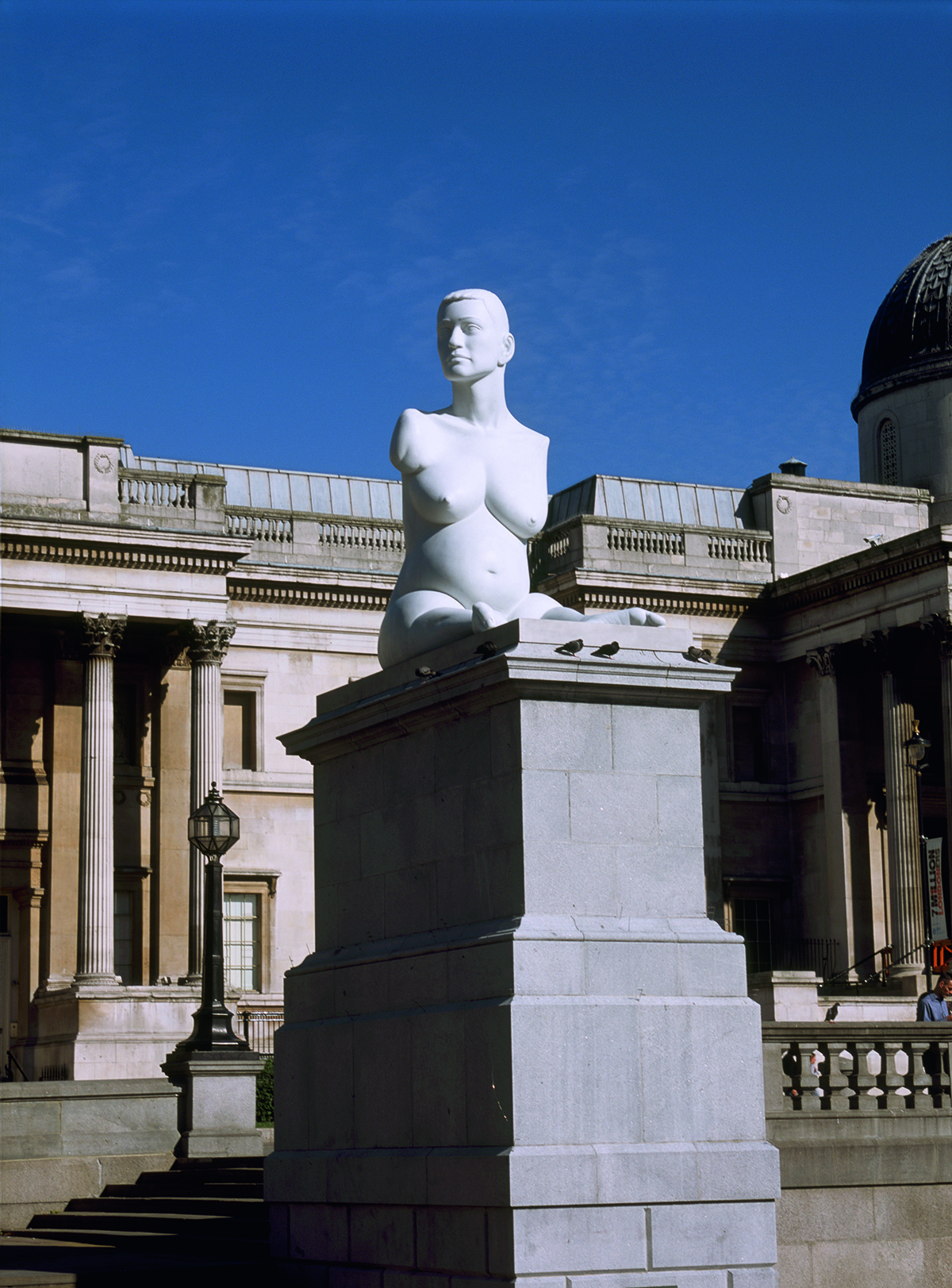

Alison Lapper Pregnant (2005). Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio. Photograph by Todd-White Art Photography
For the first in the series, I found an incredible press photo of a masked man on the streets of Hackney, which was the most iconic one. I contacted the photographer. I bought the rights to make a painting from it. And then I spent three months making a painting of it. At the end, I took all the paint that was left on the palettes and chucked it on top. It’s called History Painting (London, 8 August 2011) ROYBWN. I had this sense that the paint was disrupting it, in a way. But it was also sort of freezing it. And it was also about looking at matter. You can view it as a sculpture; when you squeeze a tube of paint, you always feel that it has so much potential. It’s about that beautiful moment before you actually crystallise it into something that may or may not be good. The paint that’s thrown on top is paint which exists as potential, as matter, as energy, as the unconscious. In a way, this process creates a screen. That screen is between the image’s dematerialised world of the image and the material world, where the paint exists straight from the tube. That was quite unconscious for me, I think. It also felt like it was about change, about movement, about how things are reconvening.
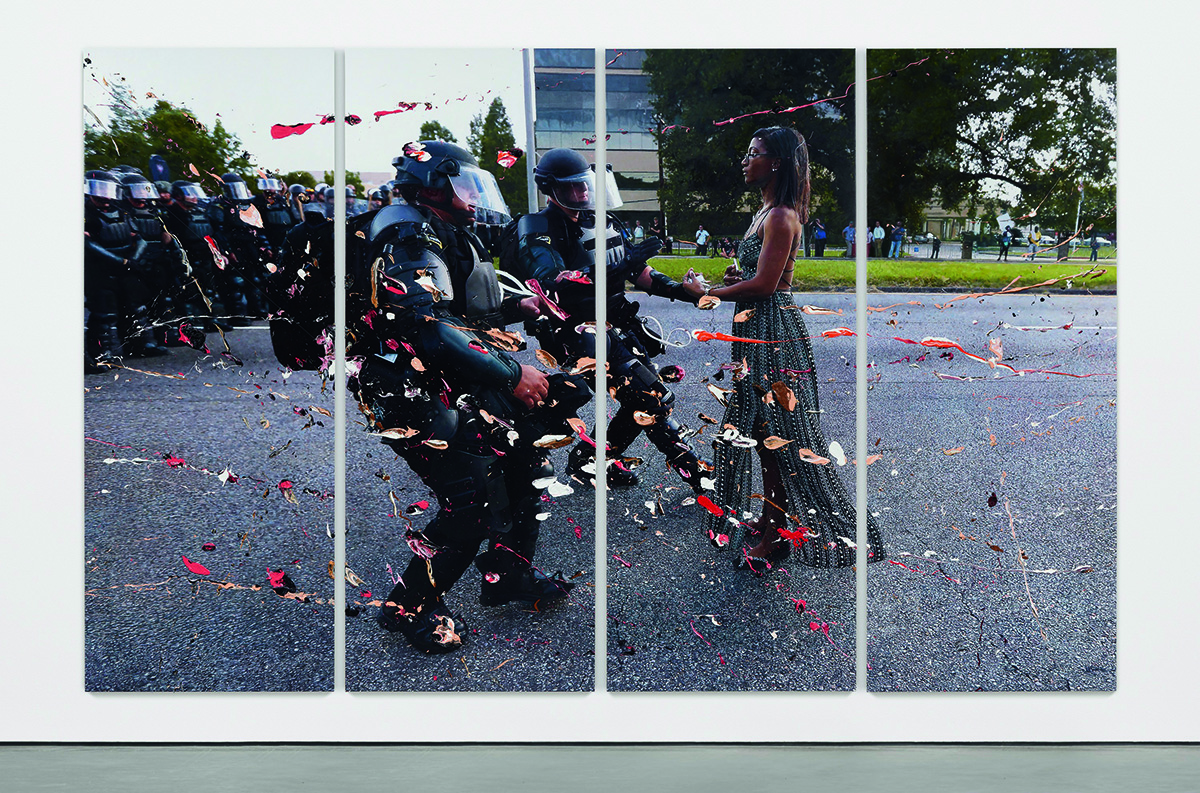

History Painting Ieshia Evans Protesting the Death of Alton Sterling (Baton Rouge, 9 July 2016) GPBW (2017). Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio
I made those types of paintings for about ten years, including a few about the Black Lives Matter movement. One painting focused on the photograph of Ieshia Evans protesting the death of Alton Sterling in Baton Rouge, an important, big picture. The large paintings would take six months to paint, so I couldn’t make that many and I had to really focus.
Read more: Gaggenau is bringing global attention to regional artisans
When the events of 2020 started unfolding, starting with Covid-19, I felt like history was in fast forward at high speed. I don’t have time to spend six months painting each picture. I have to make these in the moment. So, I had to let go of all that craft, but also of my idea of what a painting should be. I have a big printer that takes canvas, so I just thought I’d take a screenshot from my phone of events in the news as they take place, I’ll print them up and paint on top of them. This is how the Viral Paintings were born.
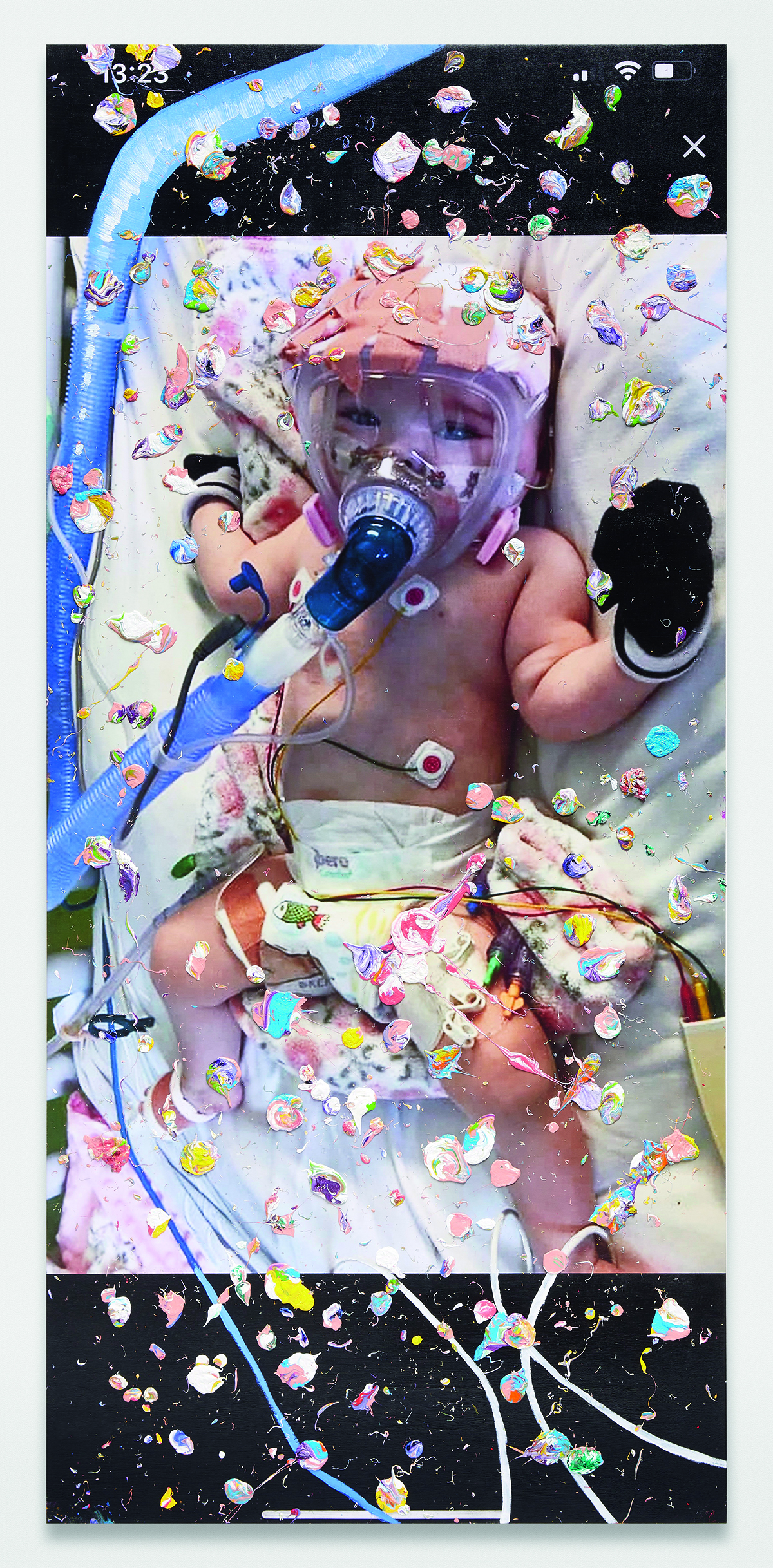
Viral Painting. Baby Erin Bates (Painted 15 April 2020), Marc Quinn, 2020. Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio
Maryam Eisler: So, you had to revisit your own practice from a whole new perspective?
Marc Quinn: Yes. It just felt so good because I went with the situation, and it took me somewhere completely new, which was really exciting.
Maryam Eisler: It’s an exciting time to be making work.
Marc Quinn: Absolutely. I always want to be excited by the work, otherwise I’d just stop. Great work has historically been produced during moments of crisis, I think. Times like these make you focus quickly on what’s important in life. And what, on the other hand, is a load of bullshit. It gets rid of a lot of fluff and noise. You also realise that your relationships with other people are important. How everyone gets along in the world and how people are treated are important. Love is important. It makes it pretty simple. Times like these bring us back to what being human is all about, and it’s an exciting time to make art because of this potential for change that seems to be all around us.
Maryam Eisler: Colonial history means that events in the US relate directly to what’s going on in the UK and in Europe.
Marc Quinn: It’s all connected – enslavement is a part of colonial history. The roots of our systematically racist present stems directly from that, a colonial history that we’re all involved in. Britain, Europe and the USA were all involved.

Viral Painting. Dazed 100, Dazed, Marc Quinn, 2020. Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio

Viral Painting. Bafta-Winning Film-Maker Becomes Hospital Cleaner, The Guardian (Painted 10 April 2020), Marc Quinn, 2020. Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio
Maryam Eisler: Tell me about the increasing importance of public art at this particular time.
Marc Quinn: It’s quite interesting to see how public art, which normally no one looks at, has suddenly taken on this urgency and this real symbolic value within society, in a way that it has never had in the past. I think that’s really interesting and it started in Bristol when they tore down the statue of Edward Colston. It’s incredible to experience the power of art in catalysing change, even if it’s iconoclasm.
Read more: Looking back on 125 years of Swarovski and into a new era
Maryam Eisler: Yes, you made a replacement sculpture. Tell me why you did that.
Marc Quinn: Jen Reid [one of the protesters] created the sculpture when she stood on the plinth and put her arm in the air. That incarnation of the artwork lasted just three minutes. When I saw the picture of her on Instagram, I immediately got in touch and asked if she’d like to collaborate and crystallise her original action for a bit longer. We then created the resin piece and put it on the plinth to activate the space. It was always conceived to be a temporary installation, to create debate about the idea of representation in the public realm and to continue the momentum of the BLM movement. We both felt it did exactly that. Its 24 hours on the plinth was enough to have the impact.
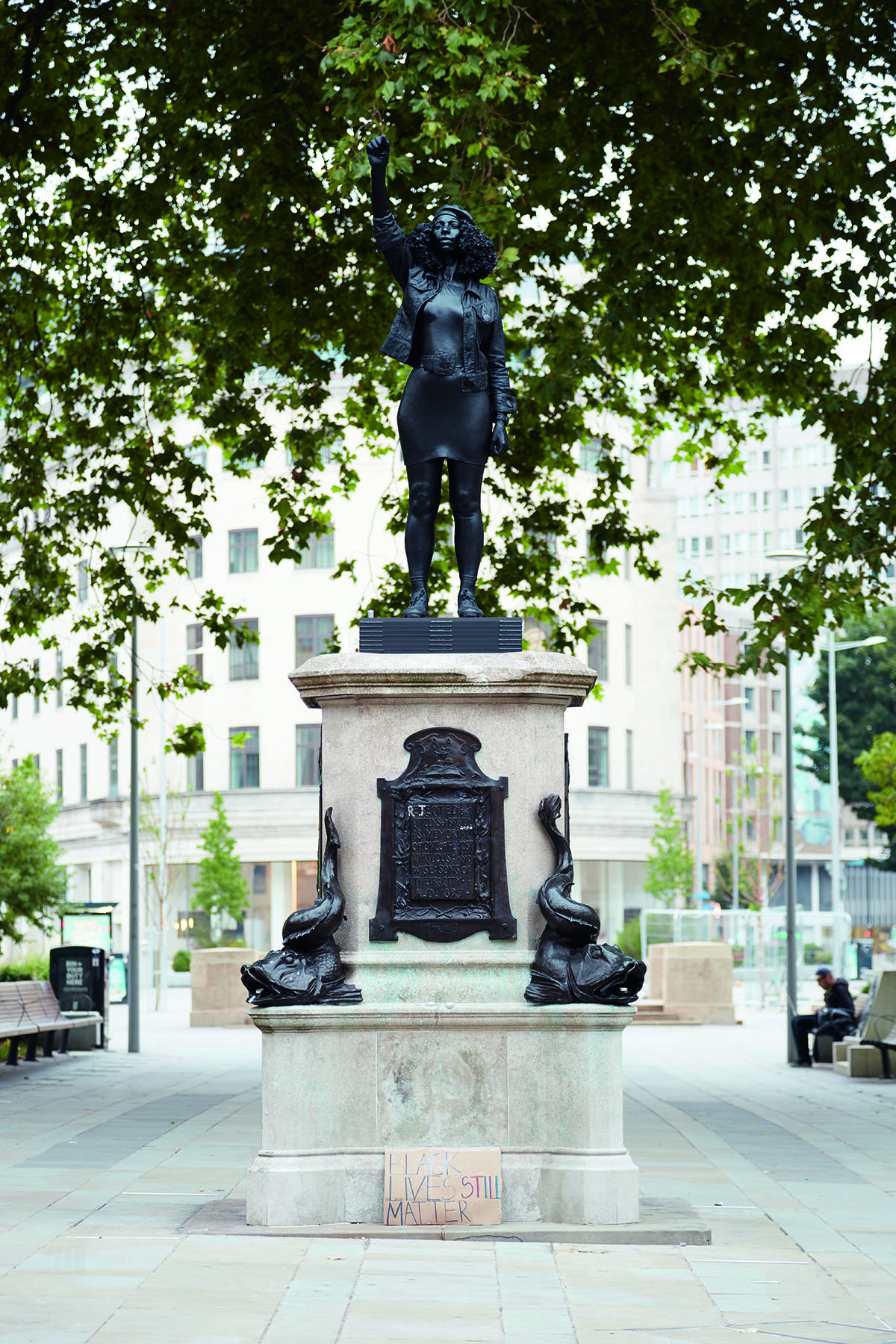

A Surge of Power (Jen Reid) 2020, Marc Quinn, 2020. Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio.
Maryam Eisler: Do you think art has been too politicised?
Marc Quinn: Most art is purely decorative and that’s not the kind of art I want to make. Art should be political. I make art about the world. I want to reflect and affect the time that we live in and the issues that are most pressing today through art.
Maryam Eisler: What effect is social media having on the art world?
Marc Quinn: Social media and the sharing of online images is great for the art world. It’s a way of making art more accessible and visible to new audiences who may not always go to a traditional gallery or museum. Instagram in particular is a brilliant platform for following emerging and established artists. Of course, as with most public forums, there can be a downside and there can be negativity.
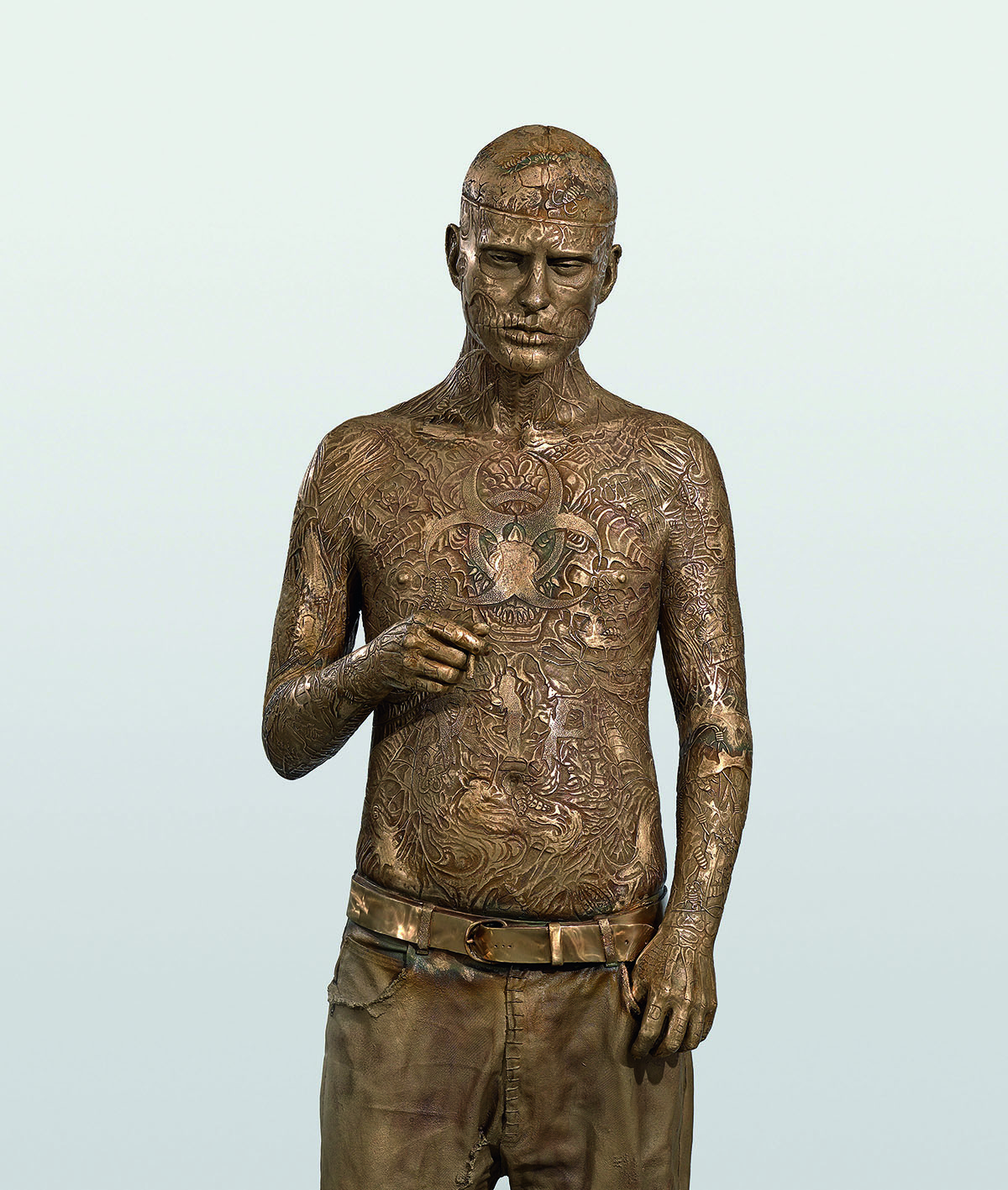

Zombie Boy (Rick) (2011). Courtesy and copyright Marc Quinn studio.
Maryam Eisler: How do you see the art world changing?
Marc Quinn: I think that there will be, and should be, a greater emergence of black artists, curators, writers, architects, and so on. Can you believe that only one per cent of practicing architects today are black? Another interesting angle is that black people and white people are coming together to talk about issues that involve us all. If you don’t do anything about it, you’re complicit in it happening. So, you’ve got to act and speak up. There is no choice. It resonated with me when [US journalist and teacher] Jelani Cobb said, “I’ve probably gotten this question 50 times from white students who ask me if it’s okay for them to write stories about people of colour and racism. And I was like, you absolutely have to write these stories.”
As a privileged successful white artist, I have access to an audience. If I don’t use that influence to talk about what matters, then what’s the point of it all? That’s what I love about the Viral Paintings – they’re tracking what I’m engaging in, now, every day.
Maryam Eisler: How do you think art history will change now, after these events?
Marc Quinn: What’s exciting is that we don’t know what the future holds, but it’s largely in our hands to open a new future and to consolidate some of the gains that have happened during this period and not just go back to the old ‘normal’.
Maryam Eisler: What about the future of museums and art galleries post-lockdown?
Marc Quinn: I think that will be really interesting to observe. No one’s really talked about it, but all the museum schedules have been completely thrown off. Most museums’ programmes work on a two- to five-year lead time, so, they can never really react to the moment. Perhaps this is a time for museums to rethink their planning and do exciting new shows that offer immediate reactions to what is happening around us. It’s an opportunity for these institutions to take an active role in the dialogue. Better representation of black curators and people in art institutions means the work of black artists can be properly contextualised and celebrated. I hope for a more inclusive art world that mirrors the diversity of the world today and celebrates artistic talent from all backgrounds and perspectives.
Find out more: marcquinn.com
This article features in the Autumn 2020 Issue, hitting newsstands in October.








