
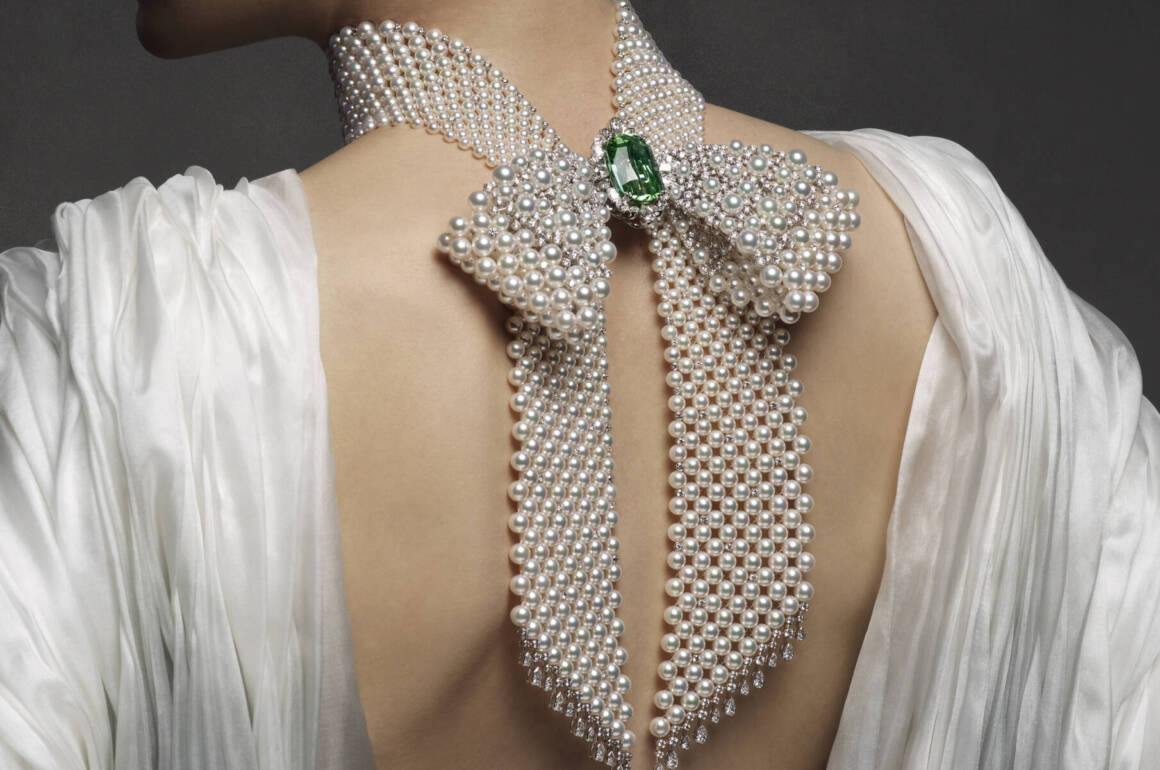
From The Bows collection, this necklace features pearls and diamonds woven together into a lace-like pattern
In creating cultured pearls, Mikimoto is focused on ocean health as well as design. Yasuhiko Hashimoto, Mikimoto Managing Director, introduces Trudy Ross to the brand’s new high jewellery collection, The Bows
LUX: Mikimoto as a brand has been concerned around marine health from the start. Why is that?
Yasuhiko Hashimoto: Our founder, Kokichi Mikimoto, invented the world’s first cultured pearls in 1893, after learning that Akoya pearl oysters were on the brink of endangerment in his hometown of Toba, due to the over- harvesting of these precious natural pearls. Mikimoto continues to honour our founder’s vision by promoting and contributing to a wide range of marine research at the Mikimoto Pearl Research Laboratory, including pearl cultivation, red tides [caused by excessive algae growth], the marine environment and more.
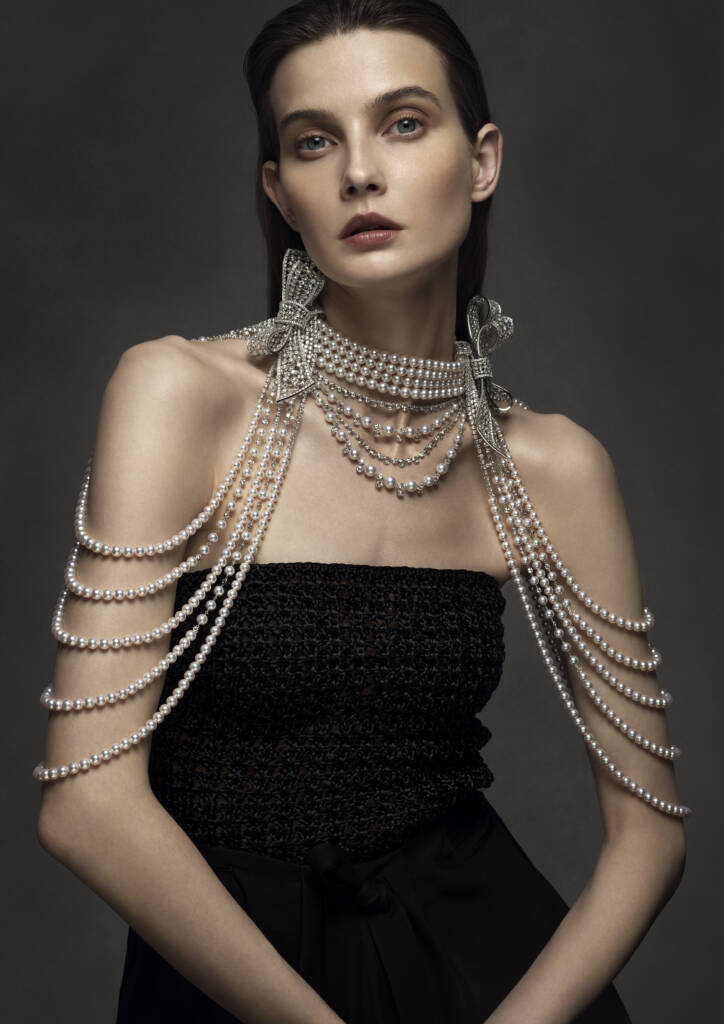

Dress jewellery designed to look like a haute couture dress
LUX: Can you tell us more about Mikimoto’s marine research and how it links to the business of pearl cultivation?
YH: We jointly developed the world’s first organic-based water quality environment-monitoring system called Kai Lingual in 2004. The system analyses the shell movement of our pearl oysters to detect sea abnormalities, such as oxygen deprivation, at an early stage, in order to minimise the impact on fisheries, including our pearl farms.
Read more: In conversation with Henry Lumby of Auriens Chelsea
And since 2009, with the cooperation of group enterprises and other companies and universities, we have successfully implemented a zero-emission pearl-farming system, so that residues such as shells, flesh, and waste emitted during the farming process are not discarded but reused and repurposed into cosmetics, food supplements, soil fertiliser and so on.
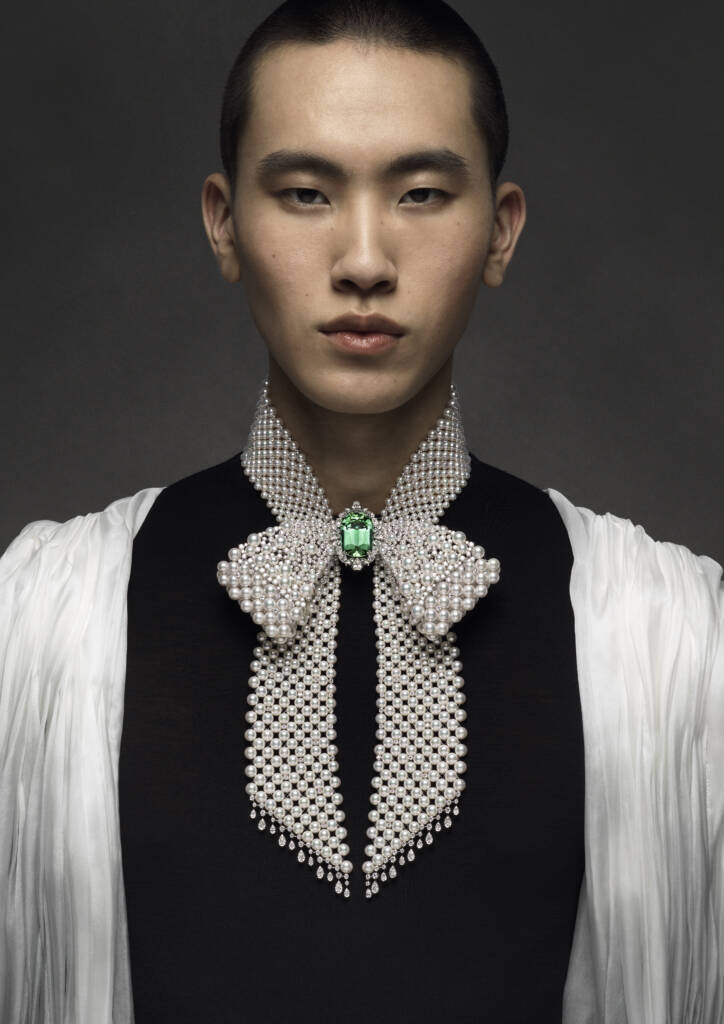

This piece from The Bows collection features akoya cultured pearl, tourmaline, diamond, and 18K white gold
LUX: What is the creative process in the design of Mikimoto jewellery?
YH: We have very talented in-house designers with a wide range of backgrounds in the arts, from Japanese style and western style to architecture and more. They draw their designs and then our craftspeople use their masterful, meticulous techniques to create the jewellery. Often, the designers will be tasked with a theme and draw inspiration from various areas. For our new high jewellery collection, The Bows, we are inspired by the natural world, especially the ocean, where our pearls are nurtured.
Follow LUX on Instagram: @luxthemagazine
Also, by going through our own archives – the brand began in the Meiji era [1868-1912] – we have seen a variety of recurring designs, including motifs of feathers and ribbons, adapting to the times, the trends and the needs of our global customers – as we have adapted them today for The Bows. So we are always open to evolving our designs and creative process accordingly.

The combination of the ribbons’ airiness and delicately-toned gemstones take inspiration from rococo-style dresses
LUX: What growing trends do you see and predict in your customer base?
YH: We can expect that the new generation of wealthy customers will expand further, especially within the Asian countries, and their sense of jewellery as a valuable asset will continue to grow. With that, their authenticity-oriented mindset will expand, too. Scarcity and the rarity value of materials, especially pearls, as a particular point of interest for consumers will therefore increase, and that means that price fluctuations will most likely be inevitable for many brands.
LUX: What does the future of luxury jewellery look like to you?
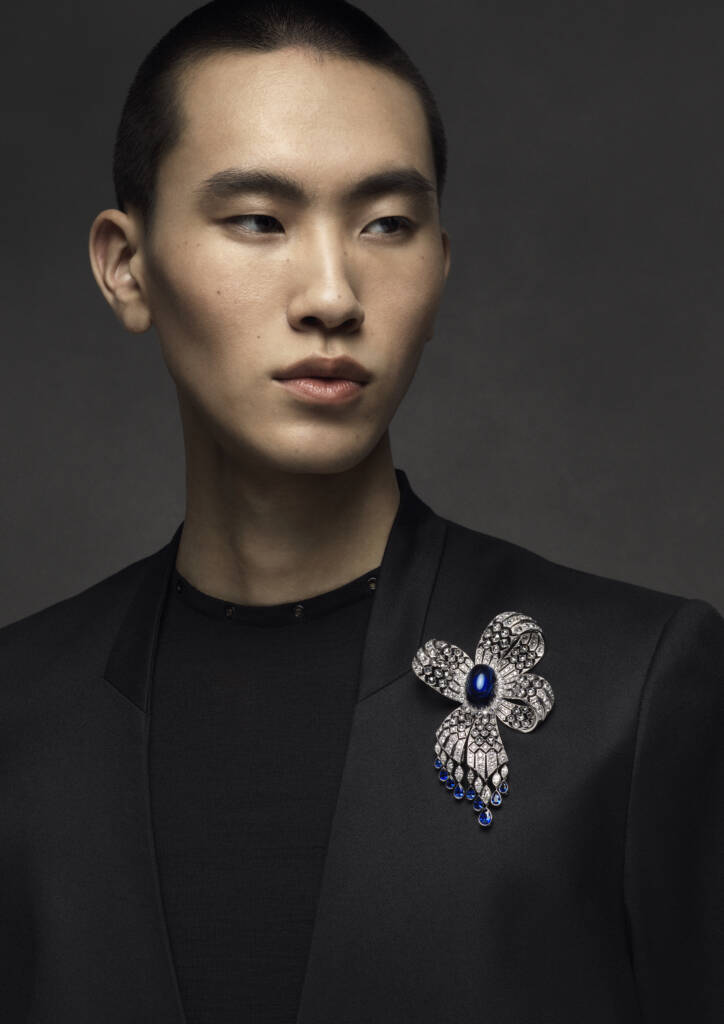

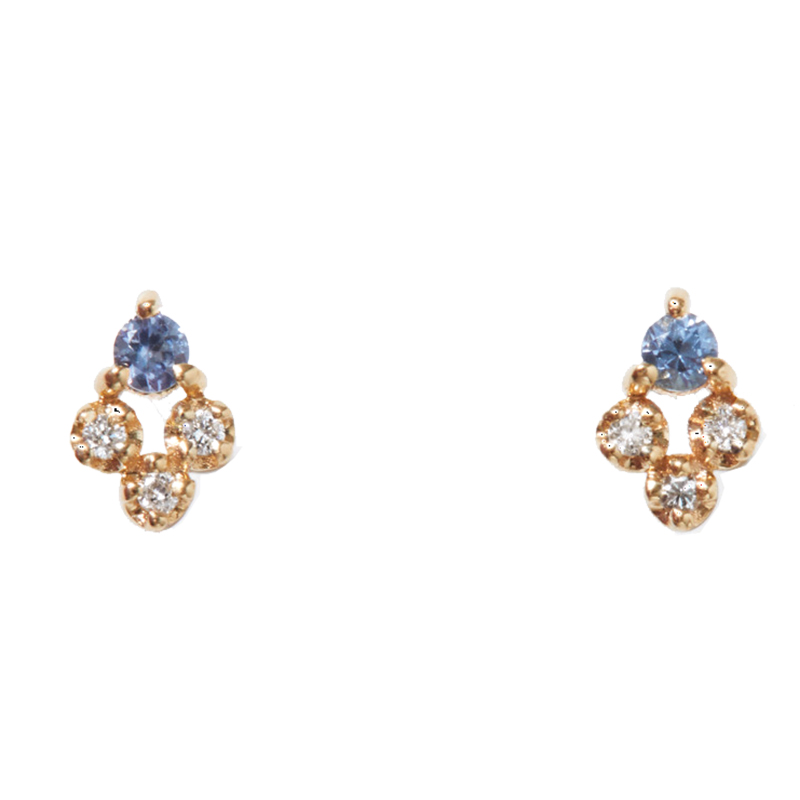
Inspired by one of Mikimoto’s archives, this piece combines akoya cultured pearl, tanzanite, sapphire, diamond, and 18K white gold
YH: In the past few years, the fashion industry has witnessed a paradigm shift, as inclusivity has become an integral essence for many brands, and genderless items and styling has become a new norm. In addition, the rapid growth of digital transformation has increased accessibility for many brands. It opens further points of contact with potential customers and increases consumer attention to brand authenticity, as well as to issues such as traceability and sustainability initiatives, and to originality.
Read more: Luxury travel from the Alps to the Persian Gulf
LUX: What’s next for Mikimoto?
YH: We are aiming to focus on creating more masterpiece levels of high jewellery, with estimated price points of more than $100 million. We hope to showcase more of the high levels of artistry in our design and craftsmanship, as well as the top-tier qualities of our materials – not just pearls but gemstones as well – and to further establish our position as a high jeweller.




















Recent Comments