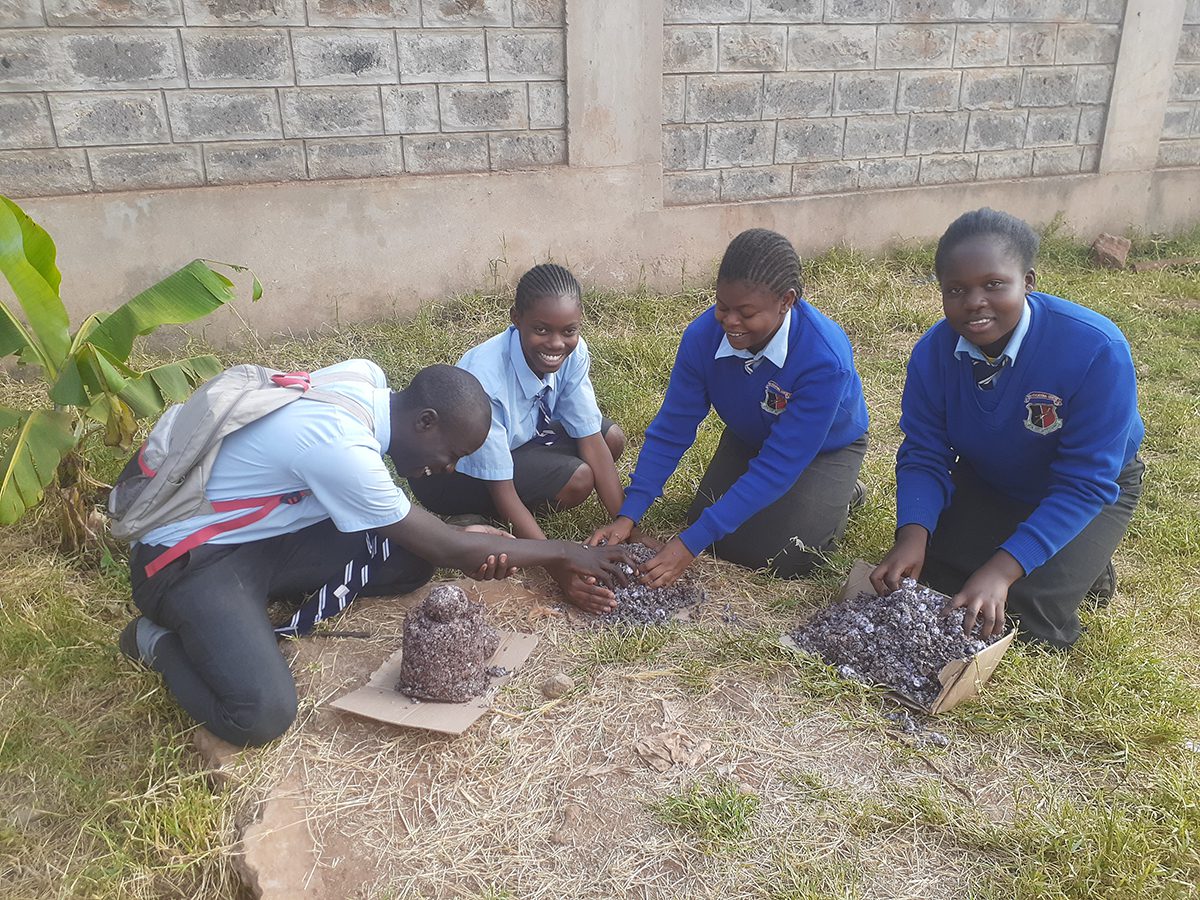

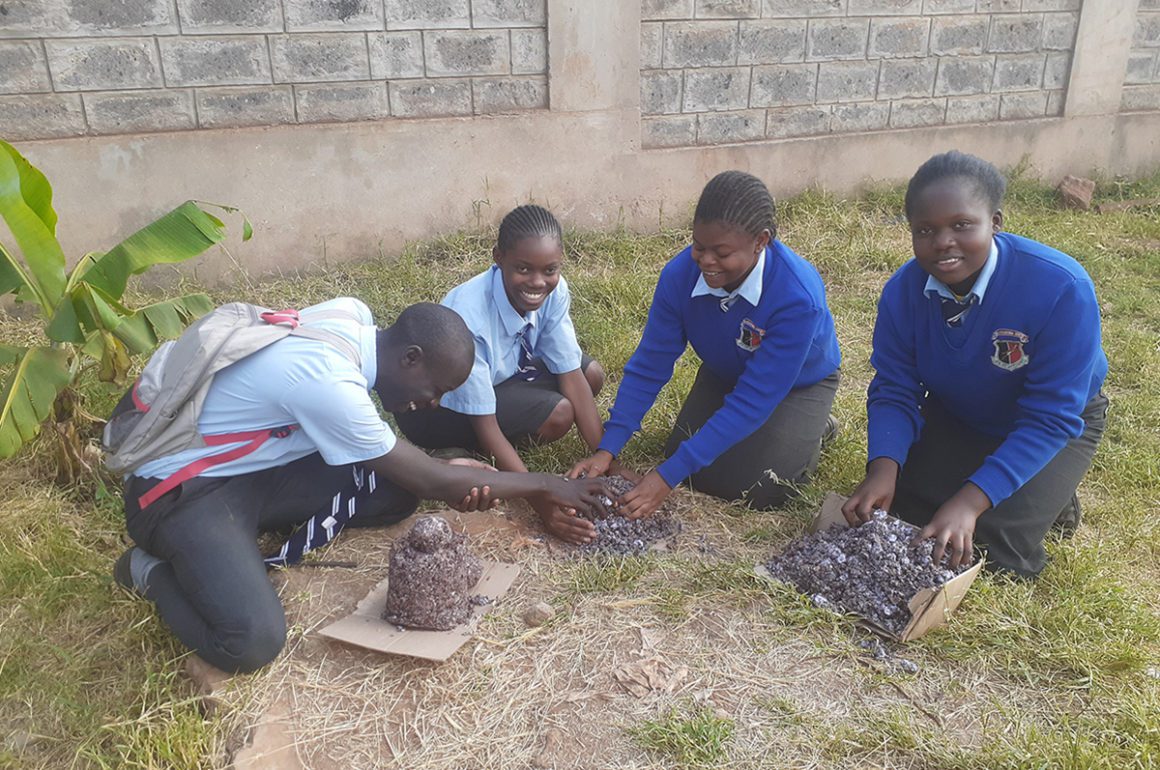
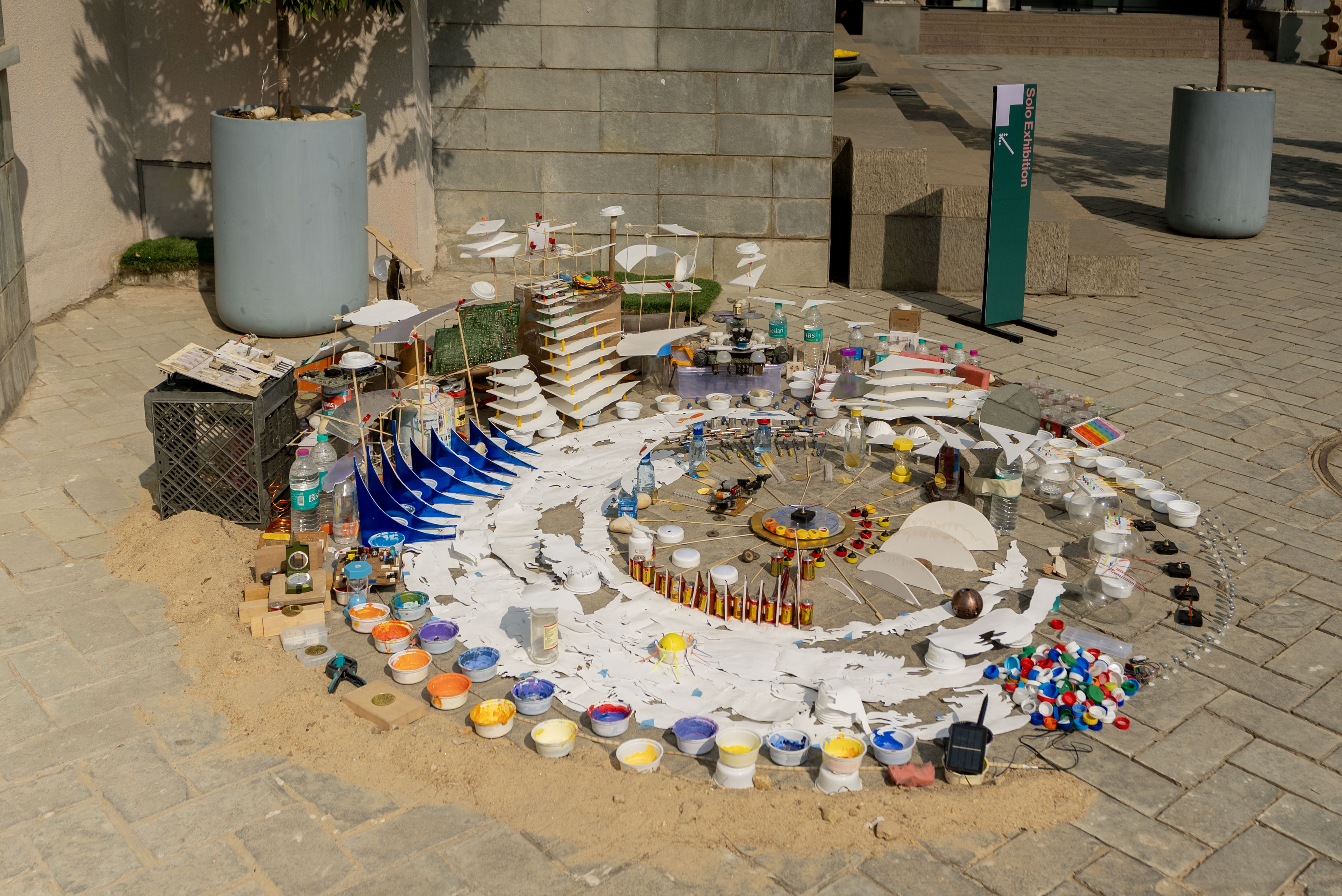
This finalist team from Kibera came up with a waste recycling system in the largest urban slum in Africa
The Earth Prize is one of the many initiatives run by The Earth Foundation. It is a competition open to all institutions from leading schools in London to the poorest slums in Africa. The Prize encourages schools, students, researchers and young entrepreneurs to educate themselves and be mentored in order to find innovative solutions to solve the planet’s environmental challenges. With the winner of The Earth Prize being announced on Friday 25th March 2022, Candice Tucker speaks to Angela McCarthy, CEO of The Earth Foundation, about the importance and impact of this Prize.

Angela McCarthy
1. Why do you think teenagers might have the solutions to some of our greatest environmental issues?
They have the ability to still think out of the box. They are in touch with their creative minds and they care deeply about the planet. This emotional intelligence is key in finding solutions. The older we get, the more we are blinded by outside belief patterns blocking our imaginations and causing us to lose touch with nature and ourselves.
Follow LUX on Instagram: luxthemagazine
2. How important is education versus action in schools with regards to the fight against climate change?
With education, action comes naturally. Once you have opened the eyes and ears of teenagers to what is happening, how and why, they can then take steps to make a change. Once they care about their planet’s crises through education, they will want to make different choices. Those choices create a ripple effect. As we know, there are many factors that contribute to climate change. If they can start to live differently or come up with new solutions, they will help the fight against climate change.

The adjudicating panel for the Earth Prize consists of leaders in sustainability, science and entrepreneurship
3. The Earth Prize is open to leading private schools in the wealthiest countries to those with the most basic education in refugee camps and slums. How do you ensure a level playing field?
Once they have registered online for free, everyone receives the same support to participate in The Earth Prize competition. This includes online video learning content and access to our 30 university mentors whom the students can ask for help at any point. I and The Earth Foundation team are available for any further advice or to answer questions that any teacher, supervisor or student may have at any time. We found that everyone was able to get access to the internet, and that is what made it all work! Our students in Lebanon had the internet go down and they would have to wait until it was rebooted, and the same happened in South Africa, but they all managed. The amazing teachers made it their mission to support their students while they came up with their own solutions. Finally, equality was guaranteed because each submission carried only a number, thus eliminating any risk of bias in the judging.
4. What was the original intention of The Earth Prize?
To inspire, educate, mentor, and empower students, schools, researchers, and young entrepreneurs with innovative ideas to tackle environmental challenges. Through this process we strive to build our very own ecosystem. Peter McGarry, the founder, and I believe in the voices of the youth being heard and bringing their solutions to life, and how everyone can be part of the solution to solving today’s most pressing sustainability issues.

The Earth Foundation was founded in 2020, in Geneva, Switzerland by Pete McGarry to encourage young people to find solutions to the Earth’s environmental challenges.
5. Apart from The Earth Prize, can you tell us about other projects within The Earth Foundation?
The Earth Prize is our first initiative. The second will be The Earth Foundation Awards that will support research endeavours in the environmental sustainability field with grants and scholarships by distributing $300,000 every year to university students and researchers. We are also in the process of creating our Alumni Association, a platform for networking and encouragement amongst our community of passionate and inspiring individuals.
Read more: Unilever’s Rebecca Marmot On The Sustainable Everyday
6. How do you ensure a long term effect and results from the prize?
Through The Earth Prize Alumni we will strengthen ties among its members, offering them access to educational content, mentorship, social events, and professional opportunities. We will be helping them bring their solutions to life, and invite them back to share their impact, successes and their challenging times to the next year’s participants. We believe this will become a very powerful way to accelerate change and showcase the leaders and change-makers of today and tomorrow.
Find out more: www.earth-foundation.org














Recent Comments